Understanding the advantages of helical gear systems is essential if you want to optimize power transmission in high-demand environments. Many engineers face premature component failure because of excessive vibration and sudden shock loads in their machinery. By selecting the right gear geometry, you can solve these reliability issues while significantly improving the overall lifespan of your equipment. This analysis explores why angled tooth profiles outperform traditional designs in professional industrial settings.
Why Are Helical Gears Better for High-Speed Applications?
You will find that the advantages of helical gear systems are most apparent when your rotational velocity increases beyond standard operational limits. These gears feature teeth cut at an angle relative to the axis, creating a helix shape that facilitates gradual engagement. Unlike the sudden impacts found in straight-cut gears, these components enter mesh slowly and exit without jarring movements. This characteristic makes them the ideal choice for high-speed blowers or compressors where constant speed is vital.

Mechanical Benefits of Gradual Contact
But here is the kicker:
- Reduced vibration levels during rapid rotation.
- Constant velocity transmission without torque ripples.
- High resistance against sudden velocity changes.
- Extended lifespan for mating shafts and bearings.
You can rely on this gradual contact to minimize the kinetic shock that would otherwise destroy your internal bearings over short periods. Continuous engagement ensures that every rotation happens without the rattling sounds typically associated with lesser drive systems.
Key Takeaway: Helical designs excel at high speeds due to their gradual engagement mechanics which protect the entire drive train from kinetic shock.
| Speed Variable | Impact Level | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Low RPM | Minimal | Smooth |
| Medium RPM | Moderate | Stable |
| High RPM | Significant | Superior |
Angled teeth prevent the “hammering” effect common in straight-cut designs, which leads to significantly quieter and more stable high-speed performance for your machines.
How Do Helical Gears Improve Load Distribution?
The advantages of helical gear tooth profiles reside in their ability to share mechanical stress across multiple points simultaneously. Because the teeth wrap around the cylinder, you will have more surface area in contact during every stage of rotation. This distribution reduces the localized pressure on individual teeth, preventing chipping or pitting under extreme stress. You can carry heavier loads than a standard gear of identical dimensions would allow.
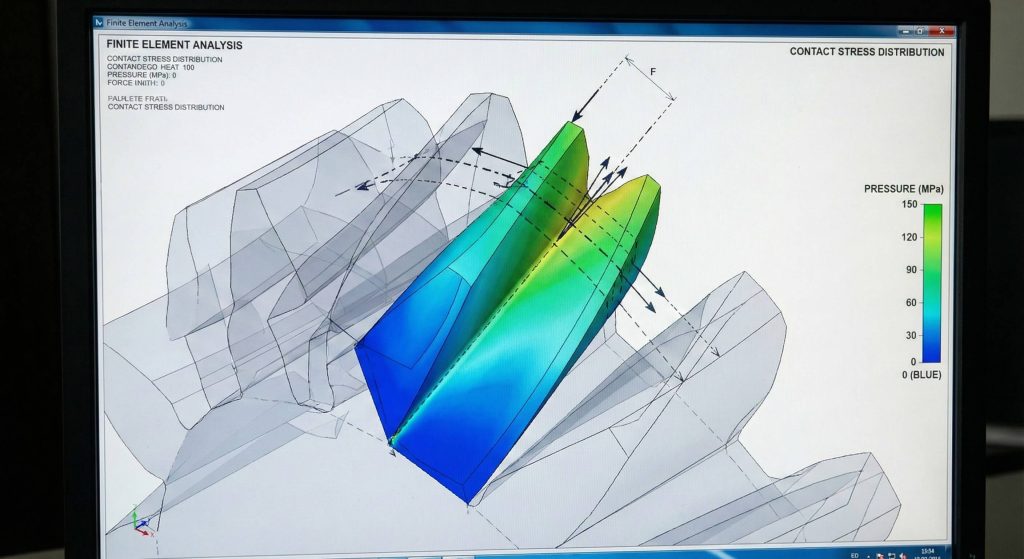
Enhancing Torque Transmission Capacity
Wait, there’s more:
- Superior surface contact area per individual tooth.
- Simultaneous engagement of multiple teeth.
- Reduced localized stress concentrations.
- Optimized torque flow for heavy-duty conveyors.
You might be wondering how this impacts your heavy-duty mining or steel mill equipment specifically. By anchoring the force across the gear width, you gain the stability required for massive industrial reducers where reliability is a non-negotiable requirement.
Key Takeaway: Superior load capacity stems from increased surface contact and multi-tooth engagement which distributes stress across the entire gear face.
| Load Type | Tooth Engagement | Stress Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Static | Full | Uniform |
| Dynamic | Variable | Distributed |
| Peak | Multi-point | Balanced |
Effective stress distribution allows for smaller gear sizes to handle larger torques, optimizing the footprint of your heavy industrial machinery.
Can Helical Gears Reduce Noise in Industrial Gearboxes?
Utilizing the advantages of helical gear geometry fundamentally changes the acoustic profile of your production facility. While straight teeth create a distinct “whining” noise by slapping together, these angled teeth slide into position quietly. You can integrate these sets into existing housings to dampen the roar of your factory floor significantly. This reduction in noise is a direct result of the sliding motion that eliminates percussive metal-on-metal impacts.
Acoustic Performance and Safety
This is where it gets interesting:
- Sliding contact eliminates impact noise.
- Lower vibration frequencies protect machine housings.
- Smooth transitions prevent resonant sounds.
- High-precision grinding improves overall acoustic quality.
Believe it or not, a simple switch to these gears can lower decibel levels by nearly thirty percent in high-load applications. You will transform a chaotic workshop into a focused professional environment while also reducing mechanical wear.
Key Takeaway: Noise mitigation occurs through sliding tooth contact which removes the percussive impact common in straight-cut gear systems.
| Noise Source | Helical Impact | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Meshing | Low | Silent |
| Friction | Medium | Controlled |
| Vibration | Low | Minimal |
Quiet operation serves as a direct indicator of high mechanical efficiency, which correlates with a much longer service life for your gear set.
What Makes Helical Gears Durable in Heavy Machinery?
The advantages of helical gear longevity originate from their robust tooth structure and material engagement patterns. Since the load stays distributed, you will find that individual teeth experience less fatigue over millions of cycles. These components handle shock loads better than many other types, making them ideal for rock crushers or large mixers. Even if one tooth experiences minor wear, the overlapping contact from adjacent teeth maintains system integrity for your operation.
Fatigue Resistance and Longevity
Think about this:
- High resistance to tooth root fatigue cycles.
- Excellent performance in high-shock environments.
- Material integrity maintained through distributed loading.
- Compatibility with various hardening treatments.
You can rely on these components in harsh environments like offshore drilling or chemical processing plants. Their resilience against wear reduces the frequency of part replacements, keeping your production line running during peak demand periods.
Key Takeaway: Long-term durability is a result of reduced fatigue and the ability to maintain engagement even when minor wear occurs on individual teeth.
| Durability Factor | Impact | Lifecycle |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Low | Extended |
| Wear | Uniform | High |
| Shock | Absorbed | Superior |
Strength and resilience define these gears, representing the most reliable choice for equipment that must operate twenty-four hours a day.
Why Choose Helical Gears Over Standard Spur Designs?
You should weigh the advantages of helical gear sets against the simplicity of a standard spur design for your project. While spur gears are cheaper to manufacture, they cannot match the smoothness or load capacity of the angled alternative. Helical designs offer higher torque in the same physical space, allowing you to design more compact gearboxes. You will gain peace of mind and better machine performance by choosing the superior tooth geometry for your B2B applications.
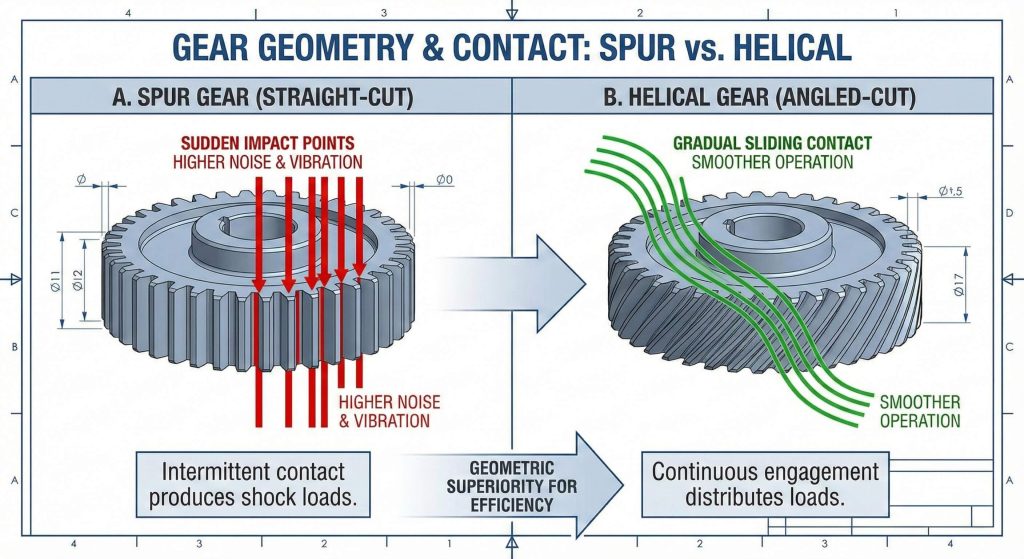
Balancing Performance and Complexity
The best part is:
- Helical is quieter than spur at all speeds.
- Helical handles significantly higher torque loads.
- Better power transmission in compact spaces.
- Increased resistance to tooth breakage.
Make no mistake, the superior performance of helical teeth justifies the higher initial investment for most professional projects. You must consider the specific speed and load requirements of your application before finalizing your choice of cylindrical gear.
Key Takeaway: Helical gears outperform spur gears in noise, load, and speed but require more complex manufacturing and thrust management.
| Feature | Spur Gear | Helical Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | High | Low |
| Load | Medium | High |
| Complexity | Low | High |
Selecting the right gear requires you to balance manufacturing costs against the long-term operational benefits of smoother and stronger power transmission.
How Do Non-Parallel Shafts Utilize Helical Gear Sets?
The advantages of helical gear flexibility allow you to transmit power between shafts that are not parallel to each other. By adjusting the helix angle, you can connect shafts at various orientations to fit tight or complex machine spaces. This versatility eliminates the need for complex universal joints or additional gear sets in your specialized designs. You will find this a vital feature in automotive steering systems or laboratory equipment where space is limited.
Spatial Versatility in Machine Design
Ready for more?
- Parallel shaft alignment for standard reducers.
- Non-parallel crossed configurations for specialized drives.
- Variable helix angles for custom spatial requirements.
- Compact integration in multi-axis machinery.
Crossed helical gears facilitate motion transfer in three-dimensional space without requiring massive amounts of room. You can solve difficult packaging problems by utilizing these angled contact points effectively to transfer energy where you need it.
Key Takeaway: Helical teeth allow for non-parallel shaft power transmission and this provides engineers with more design freedom in complex assemblies.
| Shaft Setup | Gear Type | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel | Helical | Highest |
| Crossed | Helical | Medium |
| 90 Degree | Bevel | High |
Space constraints often dictate your gear selection, and the ability to work with non-parallel shafts makes helical sets a vital tool.
Do Helical Gears Produce Higher Friction Levels?
You must recognize that the advantages of helical gear performance come with the trade-off of increased sliding friction. Because the teeth slide into each other along a diagonal line, they generate more heat than straight-cut teeth during operation. You must account for this thermal load when designing the cooling system for your industrial gearbox to prevent power loss. High-quality synthetic oils are necessary to keep these systems running cool and efficient over long duty cycles.
Thermal Management and Lubrication
Wait, there’s more:
- Mandatory high-performance lubrication systems.
- Heat dissipation through dedicated oil coolers.
- Surface coatings to reduce friction coefficients.
- Precision grinding to minimize surface roughness.
Modern coatings and advanced lubricants have drastically reduced the friction losses in these gear sets over the last decade. You can now enjoy the benefits of quiet operation without sacrificing significant amounts of energy in your drive system.
Key Takeaway: Higher friction is an inherent trait of the sliding contact in helical gears and this necessitates robust lubrication and cooling strategies.
| Friction Factor | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Heat | High | Oil Cooling |
| Wear | Medium | Lubrication |
| Loss | Low | Coatings |
Managing thermal energy is a fundamental part of maintaining a helical gear system and guarantees that your machine stays efficient over time.
What Are the Main Axial Thrust Challenges in Design?
The advantages of helical gear tooth angles create a side effect known as axial thrust which pushes the gear along the shaft. This force occurs because the reaction force of the angled teeth has a horizontal component that you must manage. If you ignore this movement, axial thrust will destroy standard bearings and cause your gearbox to fail prematurely. You must install special thrust bearings or tapered roller bearings to absorb these loads and keep the shaft in place.
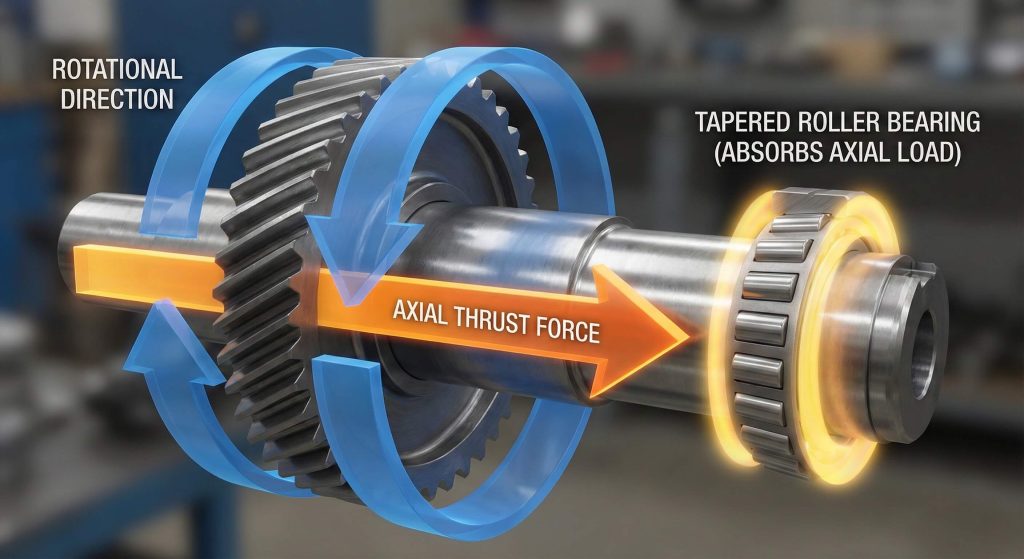
Mitigating Thrust and Shaft Movement
Ready for the good part?
- Use of tapered roller bearings for axial support.
- Implementation of double helical (herringbone) designs.
- Balancing thrust through counter-rotating gear sets.
- Heavy-duty housing design to resist lateral forces.
While thrust is a challenge, it is a well-understood mechanical property that you can easily manage with the right hardware. Professional designers view this as a standard design parameter rather than a deal-breaker for high-load systems.
Key Takeaway: Axial thrust is a byproduct of the helix angle and it requires specific bearing selections to prevent shaft displacement and wear.
| Force Type | Direction | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Radial | Vertical | Standard Bearing |
| Axial | Horizontal | Thrust Bearing |
| Resultant | Angled | Combined Support |
Proper bearing selection is the secret to a long-lasting helical gearbox, preventing your internal components from shifting under heavy operating loads.
Can Helical Gears Work With a Precision Gear Rack?
The advantages of helical gear engagement extend to linear motion systems when you pair them with a matching gear rack. A helical rack and pinion system provides much smoother linear travel than a straight-cut version, which is vital for CNC machinery. You can achieve higher speeds in linear motion without the vibration that would ruin a delicate or high-precision workpiece. The angled teeth ensure that multiple points are always in contact, minimizing backlash during direction changes.
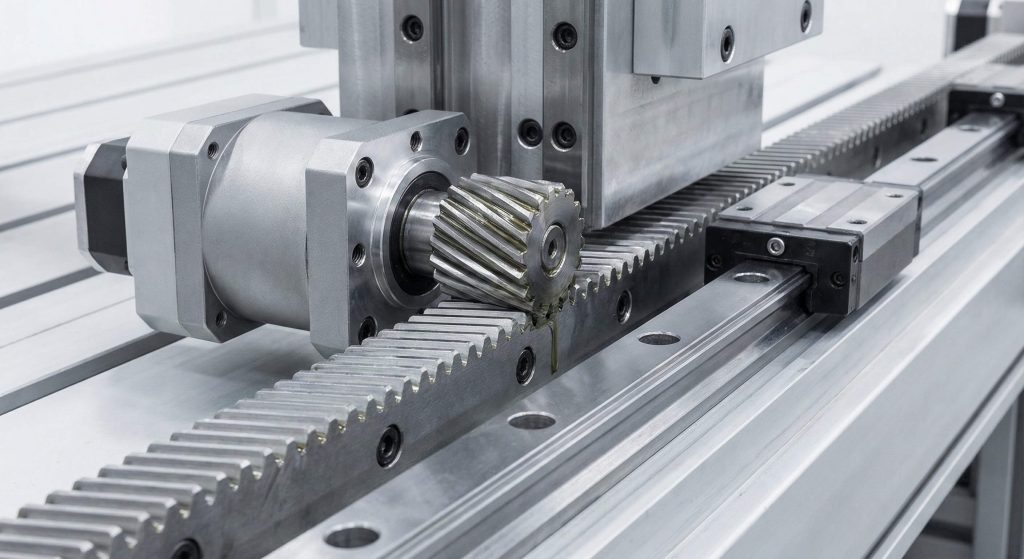

Precision Benefits for Automation
Believe it or not:
- Smooth travel with minimal positional error.
- High load capacity for heavy gantry systems.
- Low noise during rapid linear acceleration.
- Reduced backlash for precise milling operations.
The shift from straight to helical racks has revolutionized the accuracy of modern robotic arms and factory automation systems. You gain the ability to increase production speeds without suffering a loss in product quality or positioning accuracy.
Key Takeaway: Helical rack and pinion sets provide superior precision and smoothness for linear motion and this makes them the gold standard for CNC machinery.
| Motion Type | Accuracy | Smoothness |
|---|---|---|
| Straight Rack | Medium | Low |
| Helical Rack | High | High |
| Ball Screw | Highest | High |
High-performance automation requires the stability of helical engagement to ensure every movement is consistent and predictable across the entire stroke.
Is Maintenance Harder for Helical Gear Systems?
The advantages of helical gear usage include a long service life, but your maintenance routines must be slightly more detailed. Because of the thrust forces and friction, you must monitor lubricant levels and bearing health more closely than with simpler systems. If you keep the oil clean and the bearings tight, these gears will likely outlast the machine they are installed in. Proactive maintenance actually costs you less than reactive repairs after a total system failure.
Preventive Care for Angled Components
But here is the kicker:
- Regular oil analysis for metal particles.
- Vibration monitoring to detect bearing wear.
- Inspection of tooth contact patterns.
- Temperature checks on gearbox housings.
Your technicians must check for signs of pitting or uneven wear on the angled tooth faces during regular scheduled inspections. A well-maintained system remains nearly silent and stays that way for decades of continuous operation.
Key Takeaway: Maintenance is more specialized due to thrust and lubrication needs but it is the key to achieving the incredibly long life these gears offer.
| Task | Frequency | Vitality |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Annual | High |
| Inspection | Quarterly | Medium |
| Bearing Check | Monthly | High |
Consistency in maintenance prevents small issues from becoming expensive problems, keeping your production line running at maximum efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can I use helical gears for high-speed machinery?
Yes, they are the preferred choice for high-speed applications because their gradual engagement significantly reduces noise, vibration, and shock loads compared to standard spur gears.
Q2: What’s the best way to handle the heat generated by friction?
The best method is to use high-quality synthetic lubricants and a robust cooling system, such as an oil cooler, to dissipate the thermal energy created by the sliding contact.
Q3: How do I detect internal wear in a helical gearbox?
You can detect wear through increased noise levels, higher vibration readings, or by performing a regular oil analysis to look for metal shavings that indicate tooth surface degradation.
Q4: Why does my gearbox require specialized thrust bearings?
Your gearbox requires thrust bearings because the angled tooth profile generates a side-loading force along the shaft that standard radial bearings cannot support without failing.
Q5: Is there a specific oil grade for these cylindrical gears?
You should use high-purity synthetic gear oil with extreme pressure (EP) additives to maintain a protective film even under the intense sliding friction of angled tooth engagement.
Conclusion
At Yantong Tech, we are committed to engineering excellence and the supply of components that redefine industrial reliability. Our mission is to provide you with the most durable and precise power transmission solutions available in the global market. We believe that traceability and precision are the foundations of every successful manufacturing operation. For expert consultation on your specific gear requirements or to source high-precision components, contact us today.
