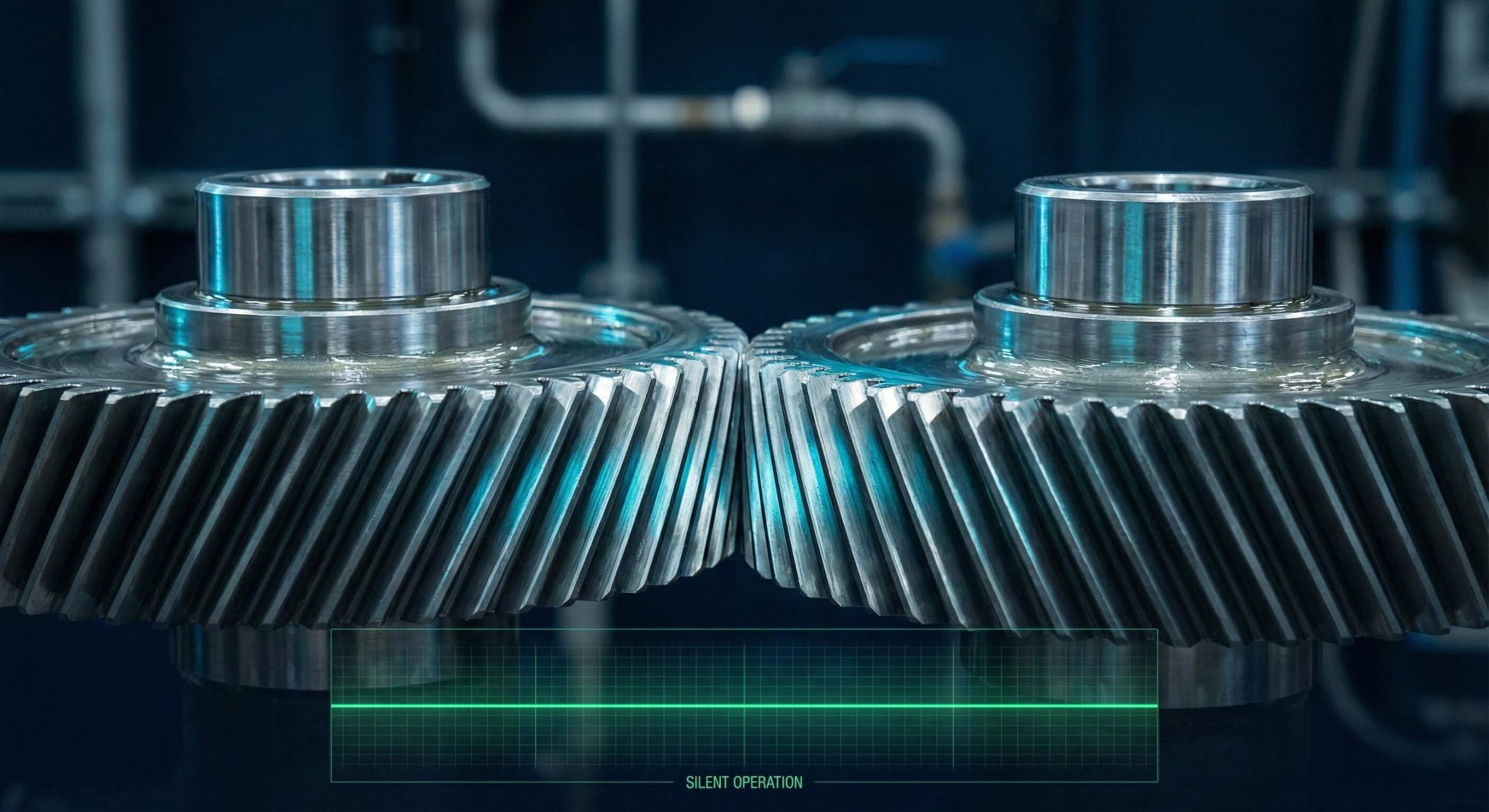

Helical gears offer superior load capacity and quiet operation due to their unique angled teeth. You might notice that straight-cut gears often produce a loud whine and high-frequency vibrations during high-speed operation. These persistent mechanical noises agitate your equipment’s internal components and lead to premature bearing failure. The strategic use of helical gear sets solves these problems by ensuring a gradual tooth engagement that distributes force evenly and runs silently.
Why is noise reduction a benefit?
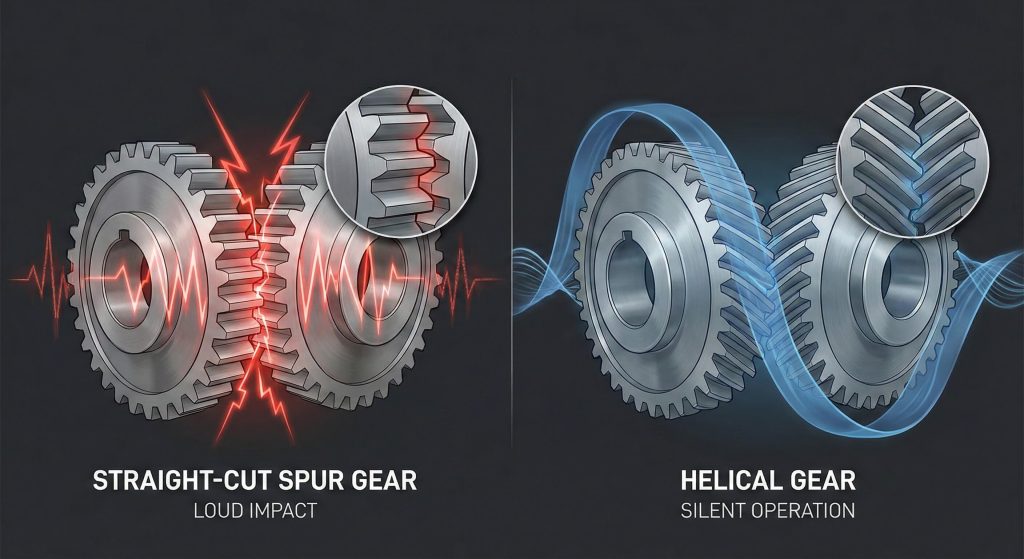
You will find that the use of helical gear systems significantly lowers the decibel levels in your facility. This reduction occurs because the angled teeth engage in small increments rather than hitting all at once.
Excessive noise often signals that your machinery is experiencing destructive harmonic vibrations. By choosing a helical design, you protect your workers’ hearing and extend the life of your housing units.
Gradual Tooth Engagement
Think about this:
The way teeth slide into mesh determines the sound profile of your entire drive train. Helical teeth use a sliding contact that eliminates the sharp “clacking” sounds typical of spur designs.
Here are the primary factors:
- Reduced impact force during meshing.
- Increased contact ratio for stability.
- Dampened mechanical vibrations.
- Optimized harmonic balance.
Key Takeaway: Lowering operational noise through helical tooth profiles improves both mechanical longevity and the safety of your workplace.
| Feature | Helical Impact | Noise Level |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth Mesh | Gradual | Low |
| Vibration | Dampened | Minimal |
This data confirms that gradual engagement is the primary driver for achieving a whisper-quiet mechanical output.
How do helical gears handle heavy loads?
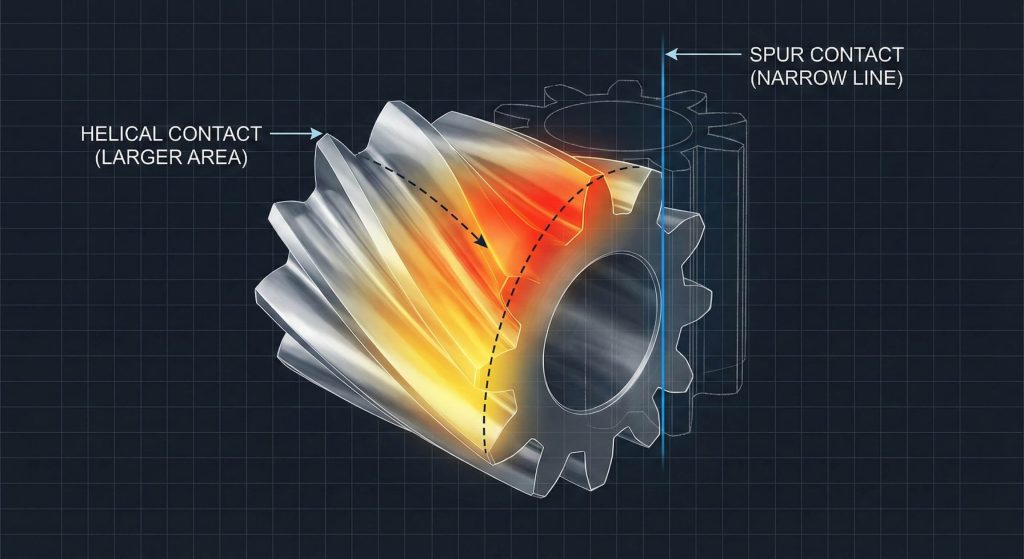
You can achieve higher torque density because the use of helical gear teeth provides a larger surface area for power transmission. The diagonal orientation means the load is shared across a longer profile than straight teeth of the same width.
This design prevents the stress concentrations that often lead to tooth breakage in heavy-duty applications. You can rely on these gears for your most demanding industrial tasks without fearing sudden failure.
Increased Tooth Contact Area
It gets better:
The helix angle allows multiple teeth to be in contact at any given moment. This redundancy ensures that the total force is never concentrated on just one single point.
Consider these load benefits:
- Higher torque carrying capacity.
- Improved resistance to shock loads.
- Even distribution of surface pressure.
- Enhanced power density per unit.
Key Takeaway: You gain superior strength and high power density by utilizing the expanded contact surface area inherent in helical engineering.
| Metric | Load Distribution | Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Area | Diagonal/Large | High |
| Pressure Point | Distributed | Low |
The increased contact area directly correlates to the gear’s ability to transmit massive torque without deformation.
Can they connect non-parallel shafts?
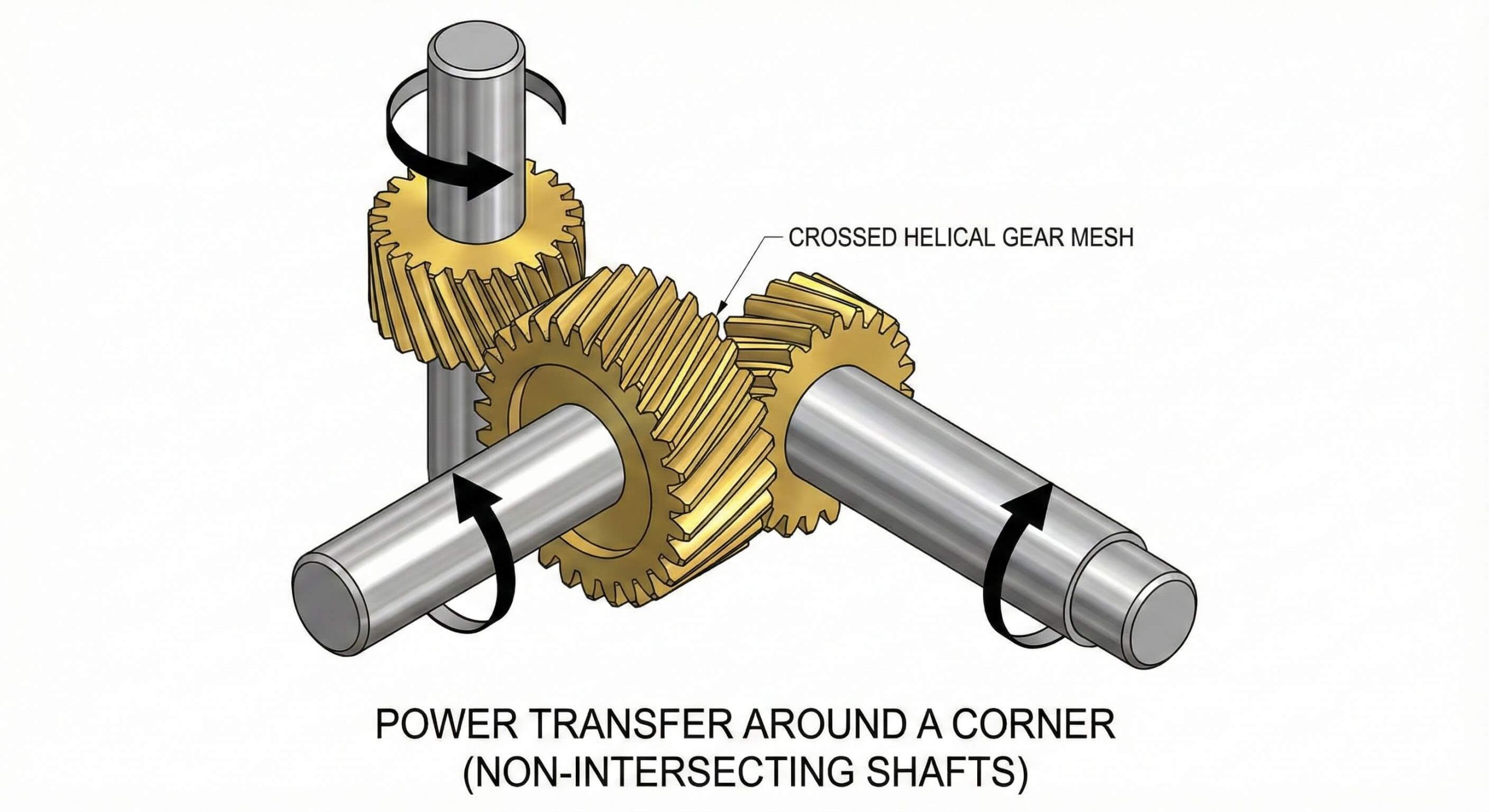
You have the flexibility to design complex machinery because the use of helical gear pairs allows for crossed-axis configurations. This means you can transmit power between shafts that are skewed or at right angles.
This spatial versatility is essential when you are working with tight footprints or irregular housing shapes. It opens up new possibilities for your mechanical layouts that spur gears simply cannot accommodate.
Cross-Axis Configuration
Look:
Standard parallel gears limit your creative freedom when designing compact robotic joints or specialized mixers. Crossed helical gears bridge the gap between perpendicular and parallel power paths effortlessly.
Why this matters:
- Enables non-parallel shaft alignment.
- Fits into irregular mechanical spaces.
- Supports complex 3D motion transfer.
- Simplifies multi-stage gearboxes.
Key Takeaway: You can solve difficult spatial design challenges by utilizing helical gears to bridge non-parallel or intersecting power paths.
| Shaft Type | Alignment | Versatility |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel | Direct | Standard |
| Non-Parallel | Skewed | High |
This adaptability makes the helical design a favorite for engineers dealing with limited installation space.
Is transmission smoother than spur gears?
You will experience a consistent flow of power because the use of helical gear systems avoids the “hammering” effect of straight-cut teeth. The smooth handover of torque from one tooth to the next ensures a steady output velocity.
This fluidity is vital for precision applications where even a tiny jerk could ruin your production quality. You ensure that your machinery runs with a level of refinement that straight gears cannot match.
Eliminating Impact Vibrations
But there is more:
The constant contact nature of these gears prevents the momentary loss of engagement that causes chatter. This leads to a more predictable mechanical performance even under varying load conditions.
Key performance points:
- Elimination of torque ripples.
- Reduced wear on drive belts.
- Improved precision for CNC tasks.
- Steady rotational acceleration.
Key Takeaway: You ensure consistent power flow and eliminate destructive vibrations by choosing helical tooth geometry for your drive train.
| Motion Type | Power Delivery | Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Impact-Based | Intermittent | Low |
| Rolling-Based | Continuous | High |
Continuous contact is the secret behind the remarkably smooth operation seen in modern helical transmissions.
Why is tooth orientation so important?
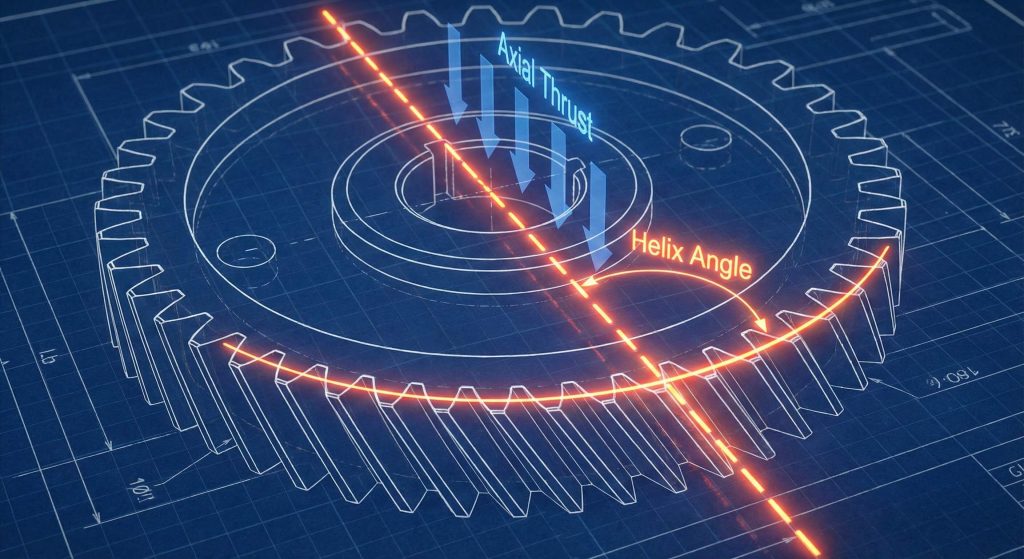

You must pay attention to the helix angle because the use of helical gear technology relies on this specific diagonal tilt. The orientation determines the balance between noise reduction and the resulting axial thrust.
By adjusting this angle during the design phase, you can tune your gears for specific performance metrics. This level of customization allows you to optimize your hardware for high speed or high torque.
The Helix Angle Advantage
Think about this:
A higher angle generally leads to a smoother ride but requires you to install more robust thrust bearings. Finding the “sweet spot” is the key to a perfectly balanced mechanical system.
Optimization benefits:
- Customized noise-to-thrust ratios.
- Scalable load-carrying limits.
- Material-specific design tuning.
- Variable gear ratio efficiency.
Key Takeaway: You can optimize your machinery for specific speed or noise requirements by precisely adjusting the gear’s helix angle.
| Angle Type | Primary Benefit | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Low Angle | Low Axial Thrust | Standard Bearings |
| High Angle | Maximum Quietness | Thrust Bearings |
The precise orientation of each tooth allows for a tailor-made approach to solving mechanical transmission problems.
What makes them durable for industry?
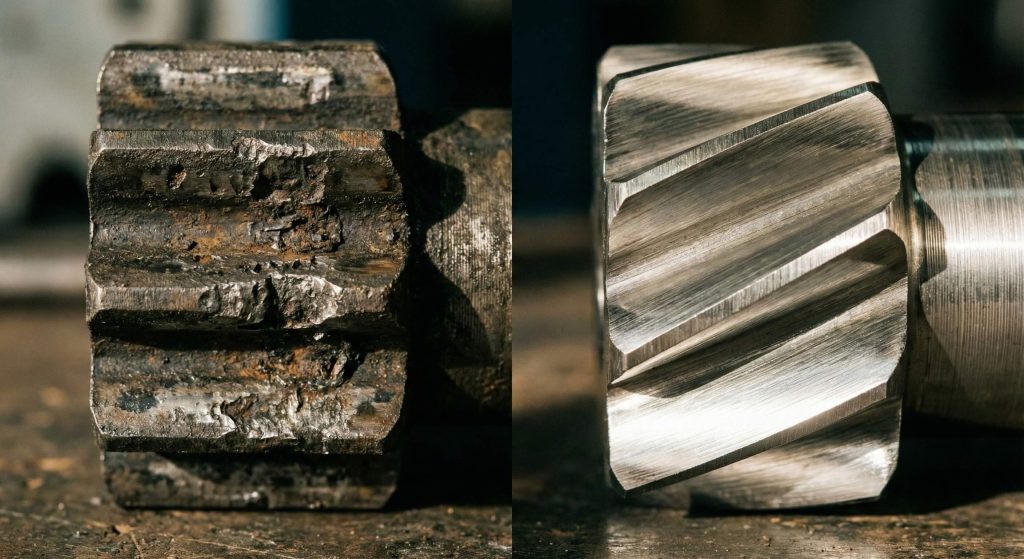

You will see a significant drop in maintenance costs because the use of helical gear components promotes uniform wear patterns. Unlike spur gears that suffer from localized pitting at the pitch line, helical teeth distribute wear evenly.
This durability means your equipment stays in service longer without needing expensive replacements or unplanned repairs. You protect your bottom line by investing in components that stand up to continuous industrial use.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Here is the kicker:
Because the teeth roll into each other rather than crashing, the physical stress is never concentrated on a single edge. This prevents the chipping and fatigue that usually end the life of straight-cut gears.
Durability factors:
- Uniform surface wear.
- High-speed operational stability.
- Better heat dissipation properties.
- Resistance to tooth pitting.
Key Takeaway: You reduce maintenance frequency and the total cost of ownership by selecting gears that naturally distribute operational stress.
| Lifecycle Stage | Helical Status | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Use | Smooth Break-in | Low |
| Long-term | Even Wear | Minimal |
Uniform wear is the hallmark of helical gears, ensuring they remain reliable throughout their entire service life.
Are helical gears more efficient?

You can maximize your system’s output because the use of helical gear sets facilitates a highly efficient rolling contact. This motion minimizes the sliding friction that often wastes energy in other gear types.
While you must manage the axial thrust, the overall energy transfer remains exceptionally high in parallel configurations. This efficiency translates directly into lower power consumption for your motors and engines.
Balancing Friction and Power
Look:
The screw-like motion of the teeth allows for a better oil film to form between the contact surfaces. This superior lubrication further reduces the drag and heat generated during high-speed rotation.
Efficiency gains:
- Lower thermal energy loss.
- Improved oil film retention.
- Higher mechanical power output.
- Reduced motor strain.
Key Takeaway: You achieve high mechanical efficiency by utilizing the rolling contact nature and superior lubrication of helical teeth.
| Parameter | Energy Loss | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | Rolling/Low | High |
| Heat | Managed | Steady |
High efficiency ensures that more of your motor’s torque actually reaches the final drive instead of being lost to heat.
Where do these gears perform best?
You should prioritize the use of helical gear systems in any application where high speed and silence are required. These gears are the standard choice for automotive transmissions and high-performance industrial gearboxes.
Their ability to handle massive loads while remaining compact makes them ideal for modern machinery. You will find them performing at their peak in environments where reliability is the top priority.
Primary Industrial Applications
Think about this:
Without helical gears, your car’s transmission would be incredibly noisy and prone to frequent mechanical breakdowns. They provide the quiet strength needed for both personal transport and heavy industry.
Common uses:
- Automotive drive trains.
- Industrial centrifugal pumps.
- Aerospace turbine systems.
- High-speed conveyor drives.
Key Takeaway: You can rely on helical gears for your most demanding high-speed and high-torque applications where failure is not an option.
| Industry | Speed Requirement | Preferred Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | High | Helical |
| Manufacturing | Continuous | Helical |
The widespread adoption of these gears across critical industries proves their unmatched performance in high-stakes environments.
How does design impact load sharing?
You gain an extra layer of mechanical security because the use of helical gear geometry ensures a high contact ratio. This means multiple teeth are always engaged, sharing the burden of the load.
If one tooth experiences a momentary spike in pressure, the neighboring teeth are already there to support it. This redundancy prevents the catastrophic failures often seen in designs where a single tooth carries the entire load.
Multi-Tooth Overlap
Here is the deal:
The overlap of tooth engagement creates a “safety net” for your gear train during sudden torque spikes. This makes your equipment much more resilient to shock loads and operational errors.
Sharing advantages:
- Redundant load paths.
- Prevention of single-point failure.
- Smoother torque transitions.
- Extended material fatigue life.
Key Takeaway: You gain a significant safety margin and smoother torque delivery through the multi-tooth contact inherent in helical engineering.
| Gear State | Load Handover | Failure Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Single Tooth | Abrupt | High |
| Multi-Tooth | Overlapping | Low |
Load sharing is the primary reason these gears can handle significantly higher stresses than their straight-cut counterparts.
Should you choose helical over spur?
You should choose helical gears if your priority is a high-performance system that remains quiet and durable. While the use of helical gear sets requires more careful bearing selection to handle axial thrust, the benefits for high-speed operation are undeniable.
Spur gears might be cheaper initially, but they cannot compete with the long-term reliability of helical designs. You are making a strategic investment in the future of your machinery by choosing the more advanced option.
Strategic Upgrades
It gets better:
Switching to helical components often allows you to downsize your gearboxes because they can handle more power in a smaller space. This helps you save on weight and material costs across your entire project.
Upgrade benefits:
- Increased system performance ceiling.
- Future-proof mechanical design.
- Higher return on investment.
- Space-saving housing sizes.
Key Takeaway: You achieve a much broader operating range and superior durability by selecting helical gears for your precision-oriented projects.
| Decision Factor | Spur Gear | Helical Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate | Exceptional |
| Long-term Value | Low | High |
Choosing helical gears over spur gears is a clear step toward modernizing your drive systems for maximum efficiency.
Conclusion
Helical gears represent the pinnacle of mechanical power transmission for modern industry. By prioritizing their use, you ensure your machinery operates with minimal noise, maximum load capacity, and unmatched smoothness. Whether you are dealing with parallel shafts in a factory setting or non-parallel configurations in robotics, the versatility of these gears is an indispensable asset for your engineering toolkit.
To ensure you select the perfect gear for your specific high-performance needs, contact us today to consult with our experts and optimize your drive systems for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I replace my existing spur gears with helical gears?
Yes, but you must account for axial thrust. Helical gears push along the shaft, so you may need to upgrade your bearings to “thrust bearings” to handle the side-load forces correctly.
What’s the best way to cancel out axial thrust?
The most effective method is using a double-helical or herringbone gear. This design features two sets of teeth at opposing angles that naturally cancel out the thrust forces from each other.
How does a helical gear differ from a spur gear in noise?
A helical gear engages progressively, while a spur gear engages its entire tooth face at once. This gradual engagement eliminates the impact “whine” and results in much quieter operation at high speeds.
Is it possible to use helical gears for intersecting shafts?
Yes, they can be configured as crossed helical gears. This allows you to transmit power between shafts that are not parallel, providing significant flexibility in your mechanical design and layout.
Which industries benefit most from helical gear sets?
High-speed industries like automotive, aerospace, and power generation benefit the most. They require the quiet operation and high load capacity that only helical tooth geometry can provide under extreme conditions.
