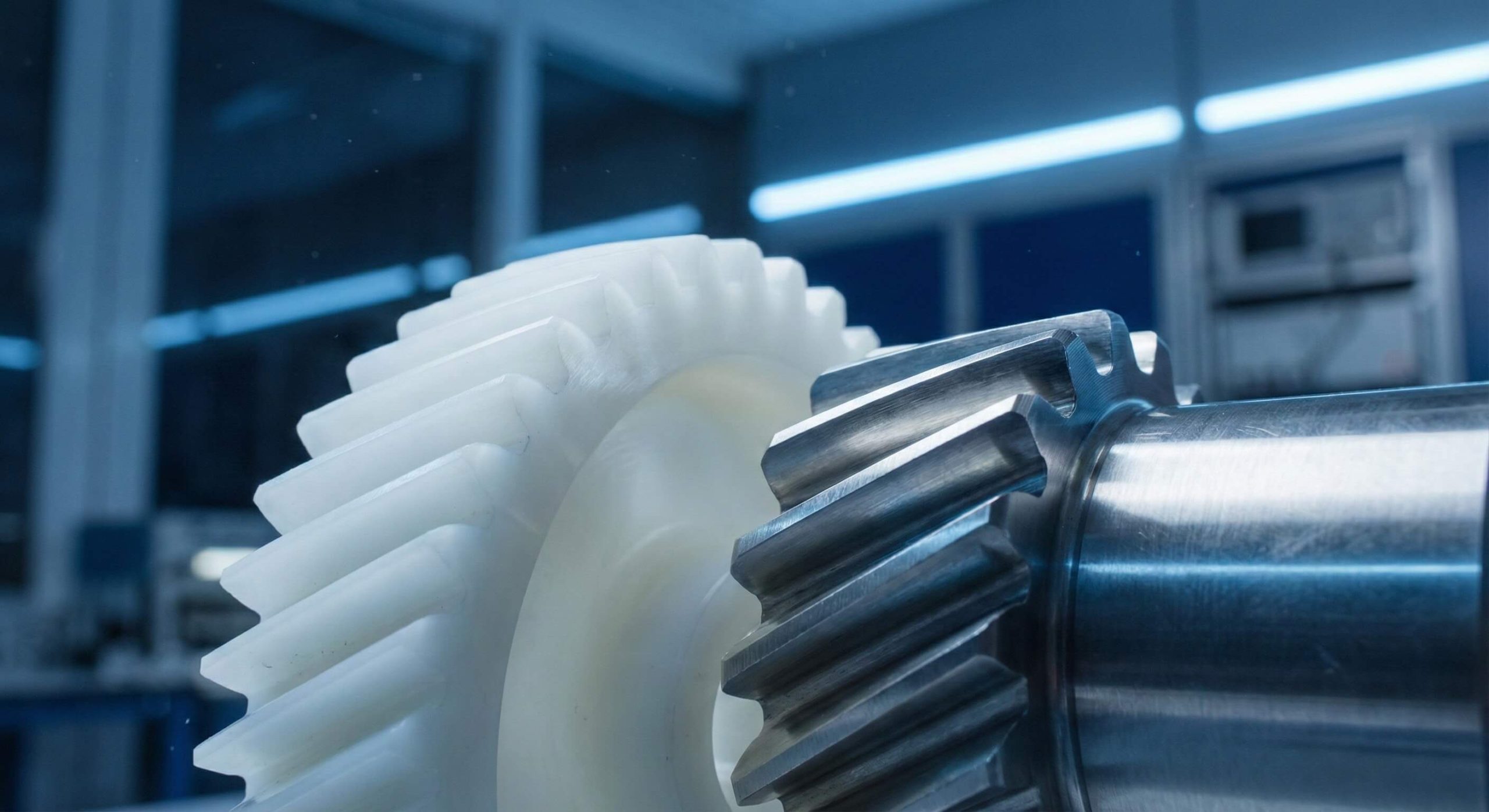
Small nylon helical gears are typically manufactured through high-precision injection molding for mass production or via CNC machining for low-volume technical applications. Many professional engineers encounter significant frustration when metallic transmission systems generate excessive acoustic resonance or suffer from lubrication failures in sensitive environments. Utilizing a premium nylon helical gear provides a reliable solution that combines self-lubricating properties with exceptional vibration damping capabilities.
How is a small nylon helical gear produced?
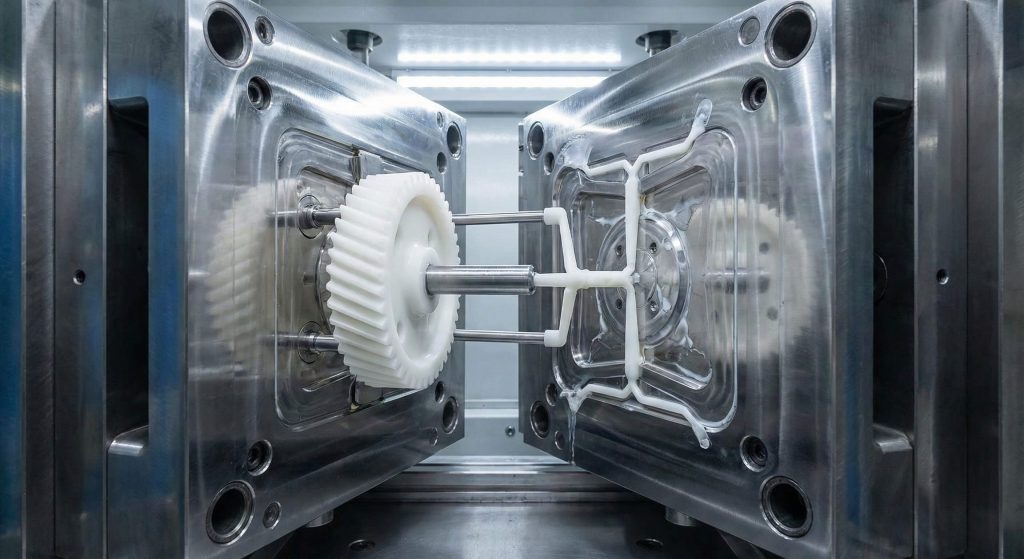
Generating a high-precision nylon helical gear often involves utilizing advanced injection molding techniques or specialized CNC subtractive fabrication strategies for lower quantities. This specific component was crafted using a precision-engineered steel mold cavity designed for managing unique shrink rates typical for thermoplastic materials during cooling. Achieving such tight tolerances requires meticulous control over injection pressure along with temperature cycles within a climate-controlled factory environment today.
You will see that resulting components offer exceptional mechanical damping plus significant weight reduction compared towards legacy steel alternatives used in high-speed transmission systems. Every single tooth profile undergoes rigorous validation for ensuring perfect mesh engagement under varying load conditions across numerous industrial applications. You can expect superior service life when these components are fabricated using top-tier resins and optimized molding parameters for high-volume manufacturing runs.
Advanced Molding Cycles
Here is the deal. While traditional methods struggle with complex tooth geometries, modern automated molding systems handle these challenges with remarkable consistency and speed.
- High-pressure polymer injection cycles.
- Automated part ejection systems.
- Controlled cooling rate management.
- Multi-cavity tool design efficiency.
Key Takeaway: Injection molding remains the most cost-effective method for high-volume production of complex polymer gears requiring consistent accuracy.
| Production Factor | Molding Metric |
|---|---|
| Volume Level | 5,000+ Units |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.03 mm |
| Cycle Duration | 45 Seconds |
| Material Waste | Minimal Recyclable |
Careful thermal management during the cooling phase prevents internal voids which could compromise the structural integrity of rotating gear teeth.
Why choose nylon helical gear materials for parts?
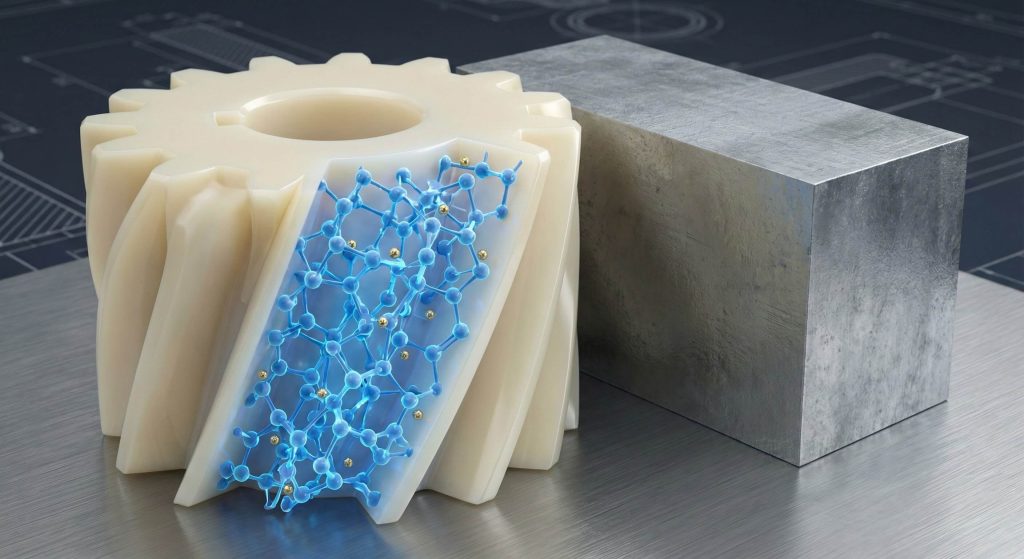
Selecting Polyamide 66 for constructing a nylon helical gear offers several distinct mechanical advantages that improve overall machine performance and operator comfort. This material possesses inherent self-lubricating properties which drastically reduce the need for messy external oils or greases in cleanroom environments. Polymer structures naturally absorb high-frequency vibrations that typically resonate through metallic gear trains during high-speed operation cycles in commercial equipment.
You will notice significant noise reduction when replacing bronze or steel components with these lightweight yet durable synthetic alternatives. Engineers favor these polymers due towards their excellent resistance against chemical corrosion and environmental humidity compared with ferrous alloys. These materials also provide a beneficial weight-to-strength ratio that lowers rotational inertia for more responsive motor control systems in automation.
Material Property Benefits
You might be wondering if plastics can truly handle industrial loads without failing prematurely under stress. The truth represents that modern reinforced polymers often outperform traditional metals in specific low-to-medium torque applications.
- Superior vibration damping capacity.
- Inherent self-lubrication properties.
- High chemical resistance levels.
- Low rotational inertia mass.
Key Takeaway: Nylon offers a unique combination of quiet operation and chemical resilience that metal gears simply cannot replicate in standard configurations.
| Material Property | Nylon 66 Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 80 MPa |
| Density | 1.14 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 260 °C |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.25 |
The molecular structure of nylon allows for gradual energy dissipation which prevents the sharp acoustic peaks commonly associated with metal-on-metal tooth contact.
When is molding best for a nylon helical gear?

Injection molding acts as the optimal fabrication strategy for a nylon helical gear when your project demands thousands of identical units. This process requires a significant upfront investment in hardened steel tooling but delivers the lowest per-unit cost across long production periods. High-volume manufacturing benefits from the extreme repeatability offered by automated molding presses which maintain consistent tooth geometry across entire batches.
You should prioritize this method when surface finish and aesthetic quality represent critical requirements for your consumer-facing mechanical assemblies. Specialized molds can incorporate complex internal features like metal inserts or intricate hub designs without needing additional secondary machining operations later. This approach effectively minimizes material scrap by recycling runners and gates back into the primary production stream for better sustainability.
Scaling Production Output
Look. If your project requires massive quantities, there represents no alternative that matches the speed and economic efficiency of high-pressure plastic injection.
- Rapid mass production speed.
- Low unit cost scalability.
- Consistent dimensional repeatability.
- Integrated hub feature options.
Key Takeaway: High initial tooling costs are quickly offset by the drastic reduction in labor and material expenses during large-scale manufacturing.
| Scaling Metric | Molding Value |
|---|---|
| Initial Tooling Cost | High |
| Labor Intensity | Low Automated |
| Surface Smoothness | Excellent |
| Geometry Complexity | High Potential |
Using multi-cavity molds allows manufacturers to produce dozens of gears in a single cycle which significantly accelerates time-to-market for new products.
How does machining a nylon helical gear work?
Producing a custom nylon helical gear through CNC machining involves removing material from a solid extruded plastic rod stock via subtractive milling. This subtractive process provides incredible flexibility for prototyping different helix angles without needing expensive permanent molds during the early design phase. Precise milling centers utilize high-speed spindles and specialized cutters for generating smooth tooth profiles with minimal heat buildup during the operation.
You can achieve much higher precision levels through machining when working with small batches or highly specialized gear geometries for research. This method eliminates the risk of internal gas pockets or sink marks that sometimes plague molded plastic parts in thick sections. Machined components offer superior mechanical strength since they retain the original grain structure of the extruded polymer material throughout their volume.
Precision Subtractive Methods
Think about it. Why spend thousands on a mold for just ten units when a CNC machine can deliver perfect results in hours?
- High precision tooth milling.
- Flexible geometry design options.
- Zero tooling investment required.
- Superior material density retention.
Key Takeaway: CNC machining represents the premier choice for low-volume production where precision and material integrity outweigh the need for mass-scale efficiency.
| Machining Aspect | Specification |
|---|---|
| Setup Duration | Short |
| Accuracy Grade | DIN 6 |
| Material Choice | Any Extruded |
| Prototyping Speed | Rapid |
Operating with sharp cutters and high feed rates prevents the nylon from melting or deforming which ensures the tooth profile remains perfectly accurate.
Can hobbing create a precise nylon helical gear?
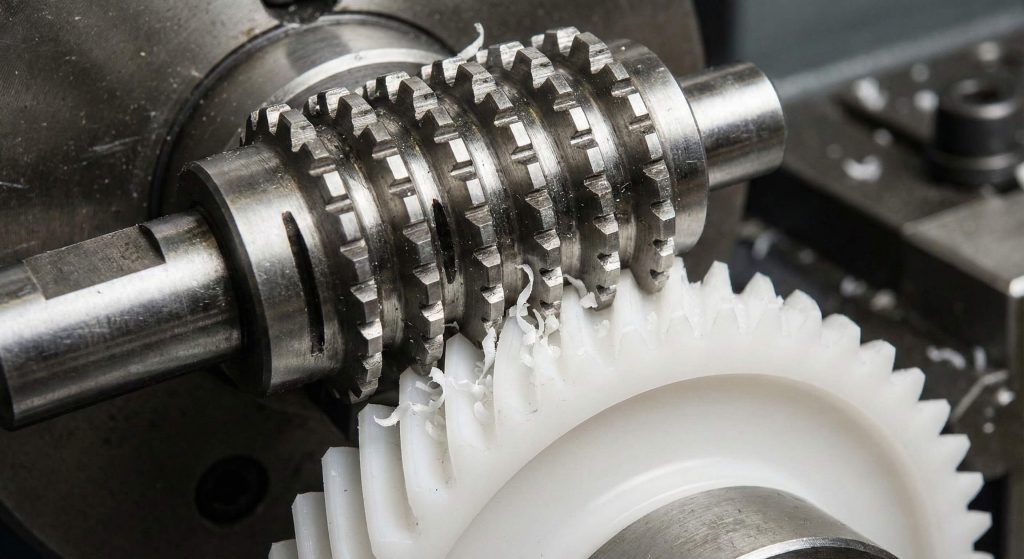

Gear hobbing creates a precise nylon helical gear by using a rotating cutting tool that progressively carves the involute tooth profile into a polymer blank. This process utilizes a rotating cutting tool called a hob that synchronizes with the gear blank for carving out teeth progressively. Hobbing produces exceptionally uniform tooth thickness and spacing which is vital for maintaining a smooth transmission of power in high-speed applications.
You might find this method superior for medium-volume runs where the accuracy of a molded part might not meet your strict requirements. Because the hob moves across the face of the blank, it creates a very smooth surface finish that reduces friction during engagement. Modern hobbing machines can handle both metal and polymer materials by simply adjusting the spindle speed and cooling fluid type for optimization.
Traditional Tooth Cutting
But here is the kicker. Even with modern tech, this classic mechanical process still offers some of the most consistent gear tooth spacing in the industry.
- Continuous cutting action speed.
- Accurate involute tooth forms.
- Excellent pitch diameter control.
- Uniform tooth thickness results.
Key Takeaway: Hobbing provides a perfect balance between the speed of molding and the extreme precision of CNC milling for specialized polymer gears.
| Hobbing Parameter | Nylon Setting |
|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | High |
| Coolant Requirement | Air or Mist |
| Surface Finish | 0.8 Ra |
| Tooth Uniformity | Very High |
Synchronized rotation between the hob and the gear blank ensures that every tooth maintains a perfectly identical profile across the entire circumference.
What challenges exist for a nylon helical gear?
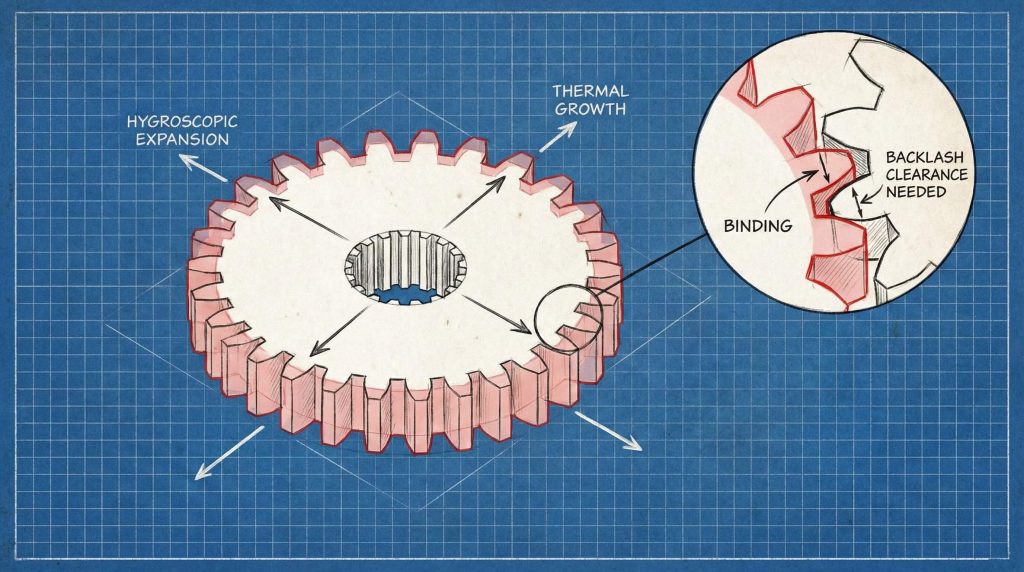
Managing moisture absorption and thermal expansion represents the primary challenge for maintaining the dimensional stability of a nylon helical gear in the field. High humidity levels can cause significant dimensional swelling which might lead towards binding within the gearbox housing if clearances remain too tight. You must also account for the relatively high thermal expansion coefficient of polymers compared with traditional stainless steel or aluminum alloys.
This means that a gear fitting perfectly at room temperature might expand and jam during continuous operation under heavy mechanical loads. Excessive heat buildup from friction can also soften the polymer teeth which leads towards premature deformation or catastrophic stripping of the gear. Engineers must utilize glass-filled resins or advanced heat-stabilized grades for overcoming these specific material limitations in demanding industrial environments today.
Overcoming Material Limits
Ready for the good part? By understanding these physical constraints, you can design smarter assemblies that account for expansion and maintain peak performance.
- Hygroscopic moisture absorption risks.
- High thermal expansion rates.
- Limited operating temperature range.
- Potential for tooth deformation.
Key Takeaway: Success with nylon gears depends entirely on proactive engineering that accounts for moisture expansion and thermal growth during the initial design.
| Challenge Factor | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Moisture Growth | Pre-conditioning parts |
| Heat Buildup | Glass fiber reinforcement |
| Dimensional Slip | Increased backlash design |
| Surface Wear | Synthetic lubrication |
Implementing larger backlash settings and verified moisture conditioning steps ensures that these components maintain their functional geometry throughout varying environmental conditions.
How to inspect a finished nylon helical gear?
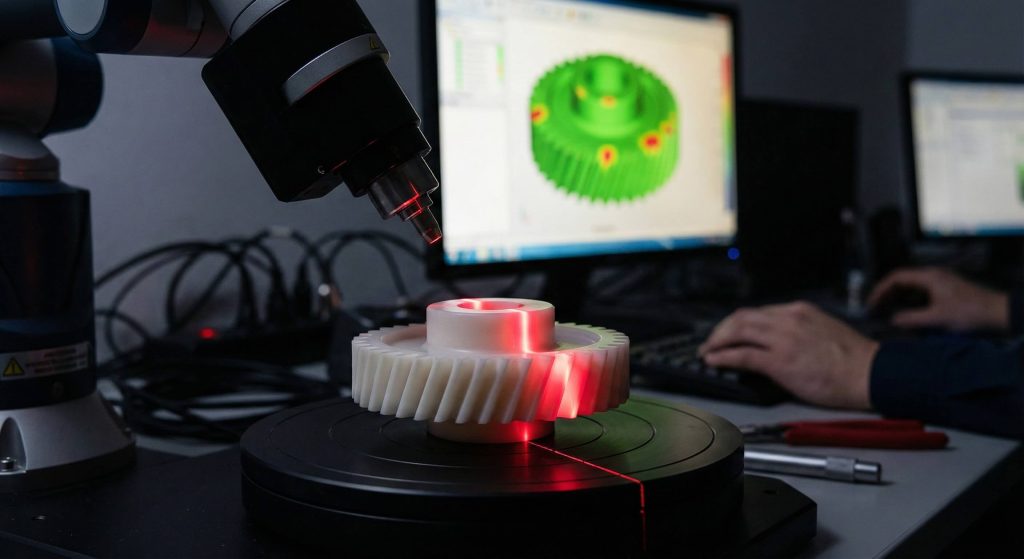
Inspecting a finished nylon helical gear requires non-contact optical measurement systems to ensure tooth profiles remain accurate without being deformed by physical probes. Using traditional mechanical calipers often applies enough pressure for slightly compressing the soft polymer which results in inaccurate or misleading dimensional readings. Optical comparators and laser scanning systems provide high-resolution data regarding the tooth profile without ever touching the sensitive surface of the part.
You should also perform rolling gear tests for measuring the composite error and ensuring the helix angle matches design specifications perfectly. Microscopic analysis can reveal hidden molding defects like internal porosity or stress fractures that might compromise the long-term durability of the gear. Documentation of these measurements provides essential traceability for critical applications in medical devices or aerospace actuators requiring high reliability.
Quality Verification Tools
This is where it gets interesting. Using light instead of metal probes allows us to see the true geometry of the gear without any interference.
- Optical profile measurement systems.
- 3D laser scanning technology.
- Rolling composite error testing.
- Microscopic surface crack analysis.
Key Takeaway: Non-contact inspection represents the only way for obtaining truly accurate dimensional data from flexible polymer components in a professional setting.
| Inspection Tool | Measured Feature |
|---|---|
| Laser Scanner | Full 3D Geometry |
| Optical CMM | Pitch and Diameter |
| Gear Tester | Mesh Smoothness |
| Microscopy | Sub-surface Integrity |
Precision measurement data helps engineers optimize the manufacturing process by identifying exactly when a mold tool starts showing signs of wear or misalignment.
Where are nylon helical gear sets used most?
A typical nylon helical gear is found most frequently in office equipment, automotive actuators, and consumer electronics where quiet operation is essential. These components exist in printers, copiers, and scanning devices where silent operation represents a primary requirement for the user experience. Automotive engineers utilize these gears for controlling window regulators, seat adjustments, and small actuators that require lightweight and reliable movement.
Consumer electronics like cameras and gaming consoles also rely on these tiny polymer parts for precise mechanical adjustments in tight spaces. Many industrial conveyor systems incorporate these gears for dampening the shock loads that could otherwise damage sensitive electronic sensors or drive motors. Their ability for operating without frequent oiling makes them ideal for food processing equipment where contamination must remain strictly controlled at all times.
Common Sector Applications
The truth is that these humble plastic parts power the quiet movements of the modern world that we often take for granted.
- Office automation equipment.
- Automotive interior actuators.
- Medical diagnostic instruments.
- Consumer electronics devices.
Key Takeaway: Nylon gears are the preferred choice for any application where noise reduction, weight savings, and clean operation are high priorities.
| Industry Sector | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Small motor actuators |
| Medical | Precision fluid pumps |
| Office Tech | Paper feeding systems |
| Electronics | Lens adjustment drives |
These gears excel in environments where people work closely with machines since they eliminate the harsh clanging noises associated with traditional metal gearboxes.
Does 3D printing suit a nylon helical gear?
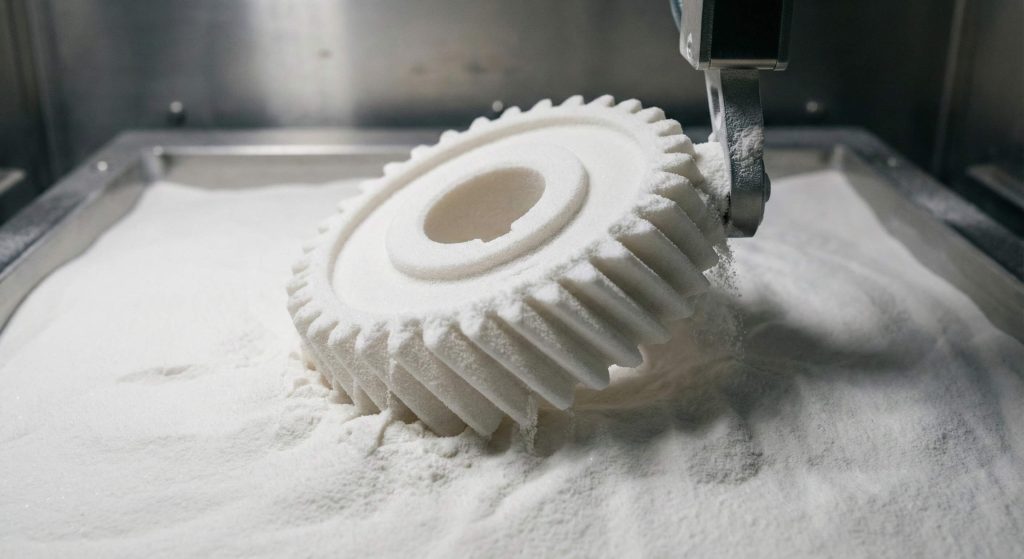

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing suits a nylon helical gear for functional prototyping and low-volume replacement parts without the need for support structures. This additive process allows engineers for testing complex internal geometries and gear ratios within hours instead of waiting weeks for custom tooling. While 3D printed parts might lack the surface smoothness of molded components, they provide sufficient strength for functional prototyping and low-speed testing.
You can use these printed gears for verifying the fit and assembly clearance before committing towards expensive mass production molding processes. It represents an excellent solution for producing replacement parts for legacy machinery where the original manufacturing drawings no longer exist. However, the porous nature of some printed polymers might require secondary coatings for achieving the same self-lubricating performance as solid extruded nylon.
Additive Prototyping Pros
In short. While printing won’t replace mass production yet, it represents an unbeatable tool for rapid iteration and creative design verification.
- Rapid design iteration speed.
- No tooling cost requirements.
- Complex geometry capability.
- On-demand replacement parts.
Key Takeaway: 3D printing serves as a powerful bridge between initial concept and final production for complex gearing systems in modern engineering.
| Printing Method | Gear Suitability |
|---|---|
| SLS (Sintering) | Excellent Strength |
| FDM (Filament) | Low Accuracy |
| SLA (Resin) | High Detail |
| Multi-Jet Fusion | Production Quality |
Advanced sintering technologies now produce parts with nearly isotropic properties which makes them much more reliable for functional mechanical testing in real-world conditions.
How to maintain your nylon helical gear properly?
Maintaining your nylon helical gear involves keeping the gear mesh clear of abrasive debris and using only plastic-compatible synthetic lubricants to prevent material degradation. Even though nylon remains self-lubricating, applying a thin layer of plastic-safe synthetic grease can further extend the service life of the assembly. You should regularly inspect the gear teeth for signs of “pitting” or thermal discoloration which might indicate excessive mechanical loads or heat.
Avoiding petroleum-based lubricants is essential since certain additives can cause the nylon for swelling or becoming brittle over long periods. Keeping the gearbox housing sealed prevents small metallic debris from entering the mesh and carving grooves into the softer polymer surfaces. Replacing worn gears before they fail completely prevents damage towards more expensive drive motors and electronic control boards within your equipment.
Longevity and Care
Wait, there is more. A few minutes of simple cleaning can prevent a major mechanical failure that might shut down your entire production line.
- Use plastic-safe lubricants only.
- Monitor for thermal wear signs.
- Prevent abrasive dust entry.
- Check for moisture expansion.
Key Takeaway: Proactive maintenance and the correct choice of lubricants are the keys for ensuring your polymer gears last as long as possible.
| Care Activity | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Quarterly |
| Cleaning Debris | Monthly |
| Re-lubrication | Bi-Annually |
| Backlash Check | Annually |
Properly maintained nylon components often outlast their metal counterparts in specific environments due towards their resilience against fatigue and corrosion over time.
Conclusion
Selecting the right manufacturing partner for your gearing needs ensures that every component meets the highest industrial standards for performance and reliability. We believe that precision engineering combined with high-quality materials provides the foundation for superior mechanical systems in every industry. Our team remains dedicated towards delivering reliable transmission components for global equipment to reduce shutdowns and rework. For more information or technical support with your next project, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I run a nylon helical gear without any lubrication?
Yes, nylon is inherently self-lubricating, but adding a small amount of plastic-safe grease can significantly reduce heat buildup and extend the gear’s service life.
How does moisture affect the size of my nylon gears?
Nylon is hygroscopic and will absorb moisture from the air, causing the gear to swell slightly, so you must design for adequate backlash to prevent binding.
What is the maximum temperature for these polymer gears?
Standard nylon gears generally operate safely up to 120°C, but specialized glass-filled or heat-stabilized grades can handle higher temperatures in demanding industrial environments.
Why use helical teeth instead of straight spur teeth?
Helical teeth engage more gradually than straight teeth, which leads to much smoother power transmission, higher load capacity, and significantly lower noise levels.
Will chemicals damage the nylon material over time?
Nylon has excellent resistance to oils, greases, and many solvents, but you should avoid exposure to strong acids or oxidizing agents which can degrade the polymer.
