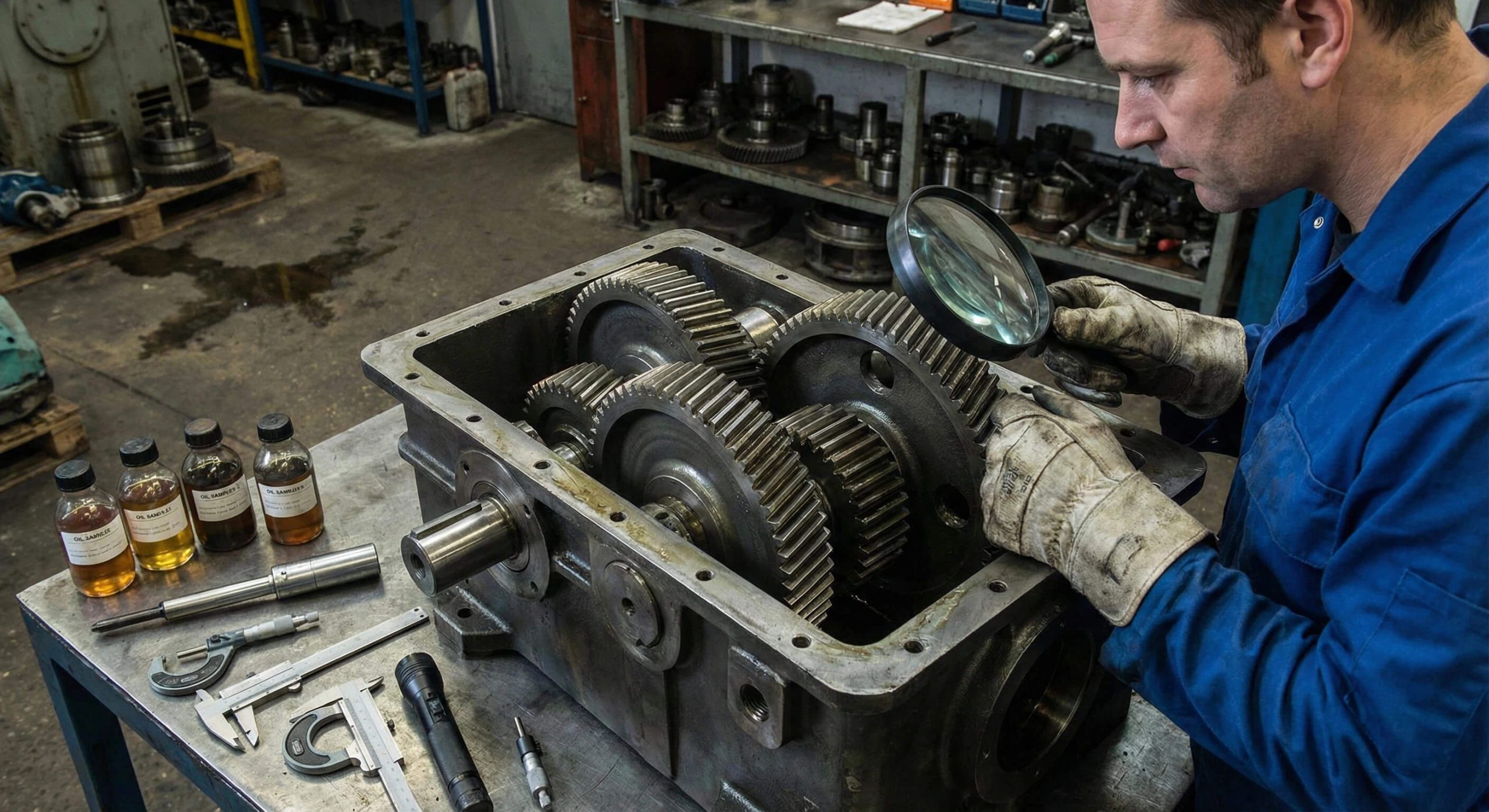

How do I analyze gear failures? You perform a systematic forensic inspection of fracture surfaces and lubricant data to identify the specific root cause of mechanical distress. Unexpected downtime destroys your profit margins and damages your professional reputation when equipment stops mid-production. Here is the deal. You can stop this expensive cycle of spur gear failure by mastering the art of forensic diagnostics today.
1. What triggers initial spur gear failure?
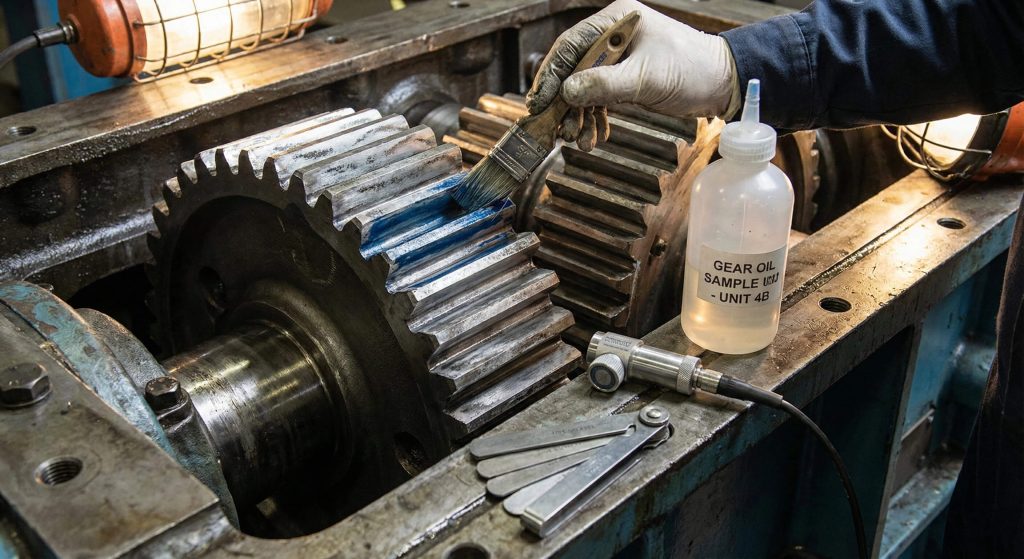

Identifying the primary driver of a spur gear failure requires a methodical approach to observing tooth contact surfaces under high magnification. These visual indicators represent a narrative of mechanical stress and thermal history within your rotating equipment housing. Wait, there is more. Catching these signs during scheduled downtime saves your facility from the high costs of emergency repairs and unexpected parts sourcing.
- Document housing temperatures during peak loads.
- Record abnormal acoustic signatures using ultrasonic sensors.
- Collect baseline lubricant samples for particle quantification.
- Photograph tooth mesh contact patterns using marking compounds.
Key Takeaway
Root cause analysis begins with visual confirmation of surface integrity and mesh alignment to identify early distress patterns before breakage occurs.
| Inspection Step | Physical Goal | Tool Required |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Audit | Detect frosting/pitting | 10x Magnifier |
| Pattern Check | Verify parallelism | Marking Compound |
| Sump Review | Find wear particles | Magnetic Probe |
2. How does bending cause spur gear failure?
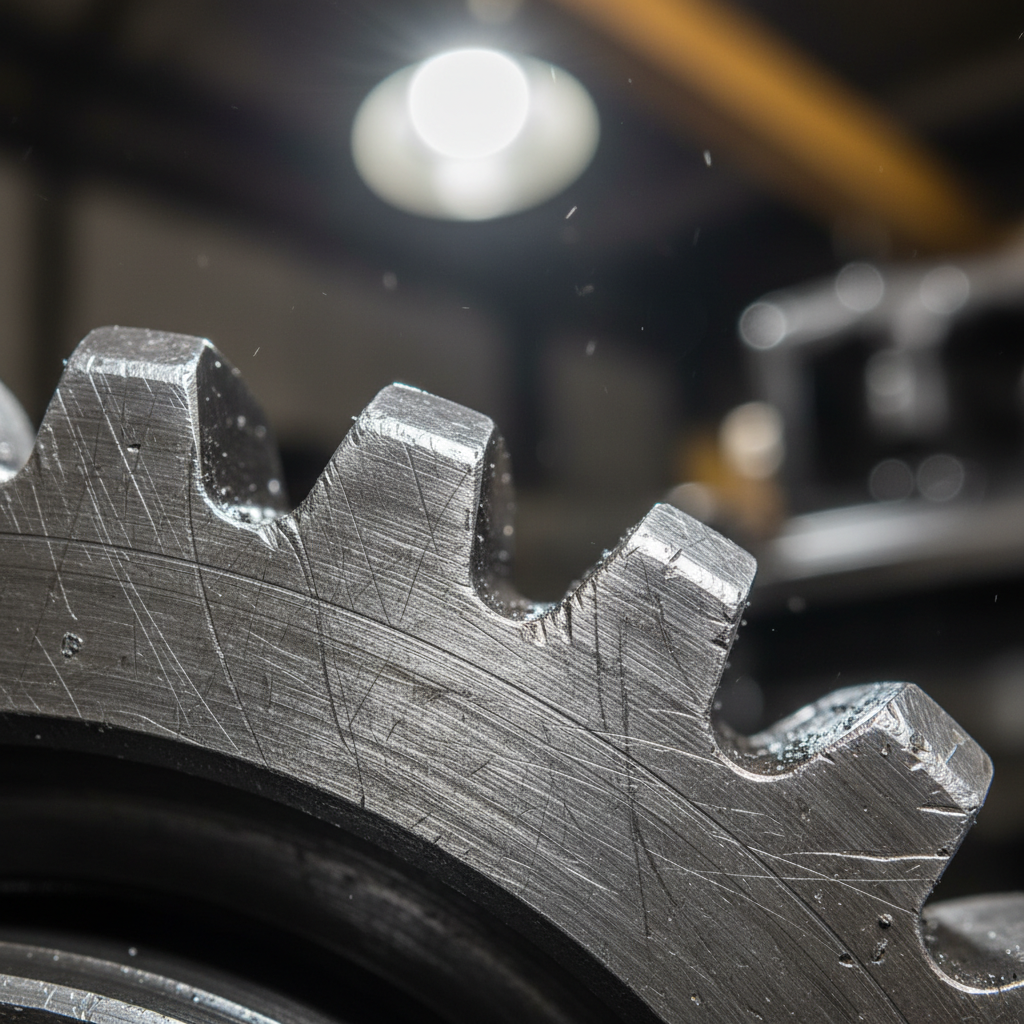

Mechanical stress concentrations at the root fillet often trigger a slow progressive fracture known as bending fatigue. This specific mode originates where the tooth meets the gear body because cyclic tension exceeds the material strength. Think about it. You can identify this damage by looking for smooth beach marks that radiate away from the crack initiation point.
- Inspect root fillets for grinding burns or tool marks.
- Measure residual stresses using X-ray diffraction techniques.
- Verify the carburized case depth matches engineering drawings.
- Monitor vibration sidebands for early crack detection signals.
Key Takeaway
Bending fatigue leaves distinct beach marks indicating a progressive failure that you can prevent through optimized root geometry and material quality.
| Fatigue Signal | Appearance | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Beach Marks | Concentric ridges | Cyclic propagation |
| Ratchet Marks | Vertical steps | Multiple origins |
| Brittle Zone | Crystalline shine | Final snap |
3. Why does surface pitting signal spur gear failure?
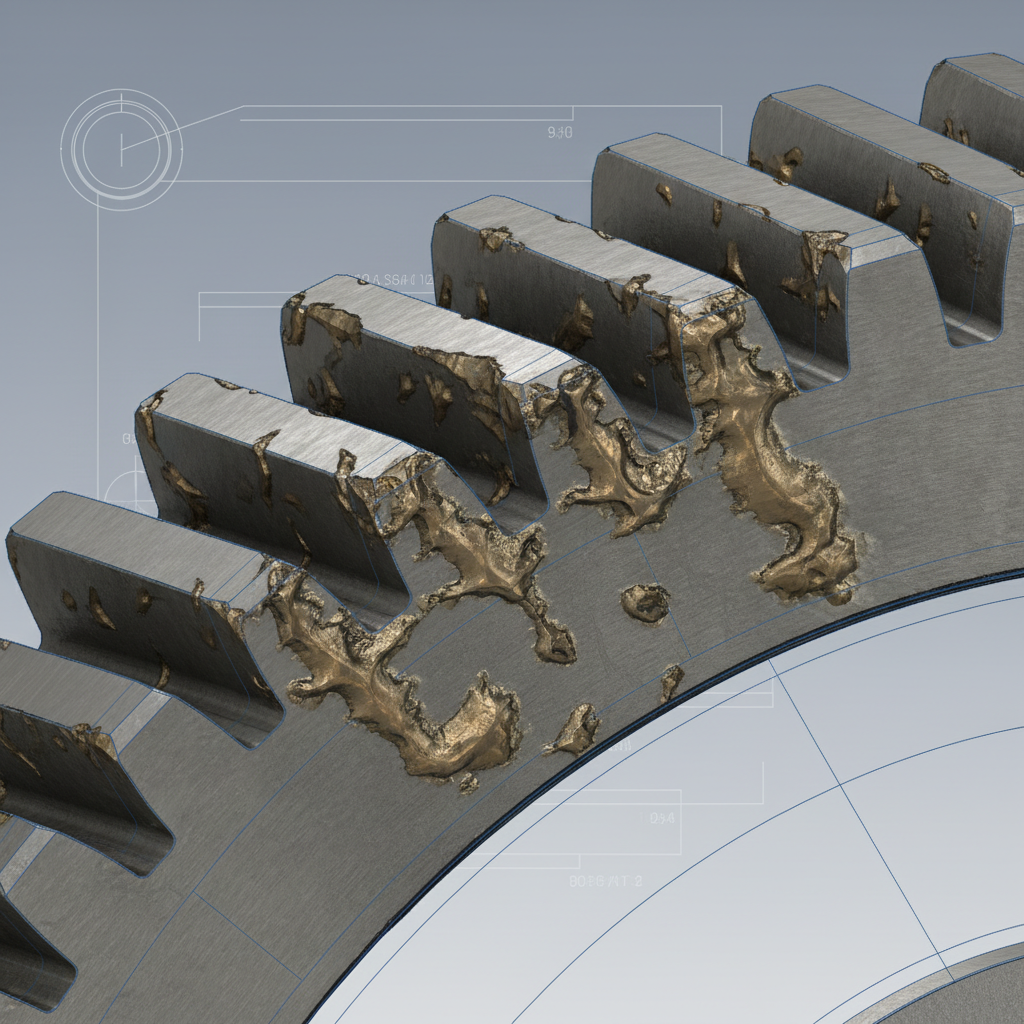
Repeated contact stresses on the tooth flanks eventually cause small fragments of metal to break away, signaling a spur gear failure. This mechanism starts as microscopic cracks that form beneath the surface where Hertzian pressure is highest during mesh. Ready for the good part? You can often stop this process by switching to a lubricant with better surface-active additives.
- Identify macropitting craters larger than one millimeter.
- Check for spalling where pits coalesce into large craters.
- Monitor vibration levels at the gear mesh frequency.
- Assess the lubricant film thickness at the pitch line.
Key Takeaway
Surface pitting signals a failure in the material’s contact fatigue resistance, requiring immediate attention to lubricant quality and load distribution.
| Pitting Stage | Dimension | Urgency |
|---|---|---|
| Frosting | Microscopic | Monitor |
| Macropitting | > 1 mm | Investigate |
| Spalling | Large Craters | Replace |
4. When does lubrication lead to spur gear failure?
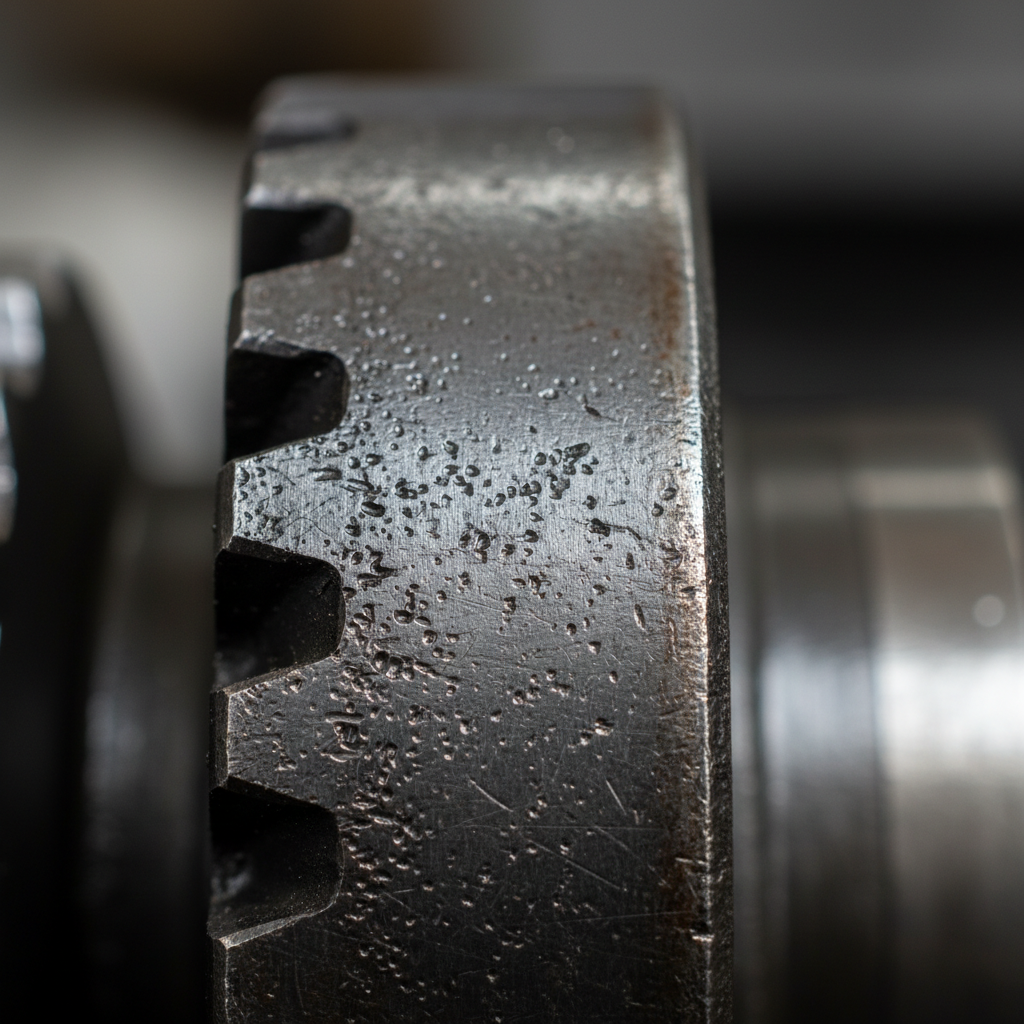

Maintaining a consistent oil film represents the most important factor for preventing premature breakdown in your facility. You might experience boundary lubrication issues when your oil viscosity is too low for the pressures generated at the mesh point. What is the real story? Proper prevention involves selecting fluids with extreme pressure additives to protect surfaces during high-load moments.
- Analyze oil for silicon levels indicating dirt entry.
- Check for iron particles representing internal wear.
- Monitor water content for corrosion and film issues.
- Verify additive levels through periodic lab testing.
Key Takeaway
Lubrication failure is a major driver of gear damage that you can manage through precise viscosity selection and rigorous contamination control.
| Lubricant Issue | Physical Effect | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Viscosity | Frosting/Wear | Increase Grade |
| Dirt/Sand | Abrasive Grooving | Better Filters |
| Water Entry | Corrosion/Pits | Seal Repair |
5. Can heat cycles accelerate spur gear failure?
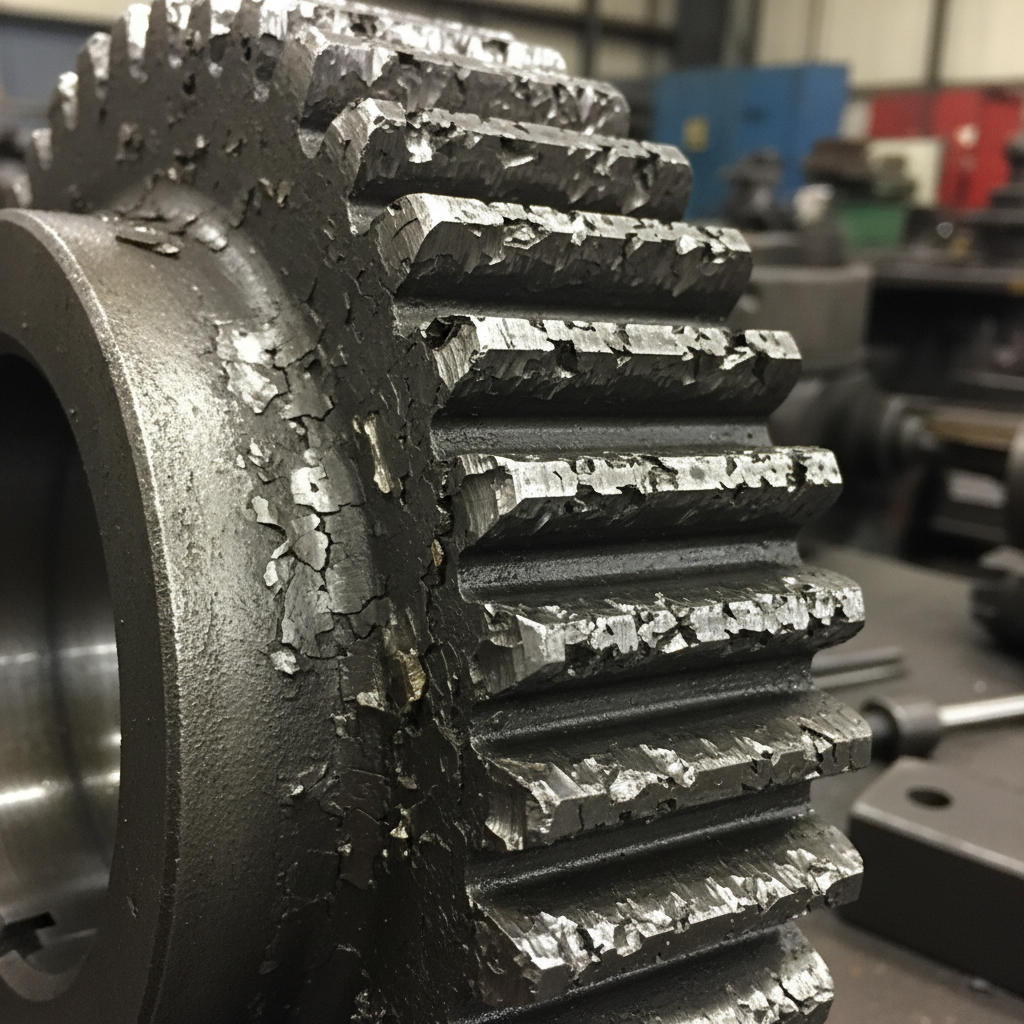

Excessive operating temperatures thin your lubricant and reduce its ability to prevent a catastrophic spur gear failure. You might observe that heat causes the metal to expand and reduces the backlash between your meshing gears until they jam. Wait, there is more. Long-term exposure to high heat can even soften the hardened surfaces of your gears and lead to rapid deformation.
- Monitor housing temperatures during the hottest shifts.
- Check for discolored or burnt-smelling lubricant.
- Inspect for thermal cracks on the gear tooth surfaces.
- Verify the cooling flow rate to the gear mesh point.
Key Takeaway
Heat cycles degrade lubricant performance and metal hardness, making thermal monitoring a vital part of your gear failure prevention strategy.
| Thermal Driver | Sign of Failure | Preventive Step |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | Temperature Spike | Add EP Oil |
| Expansion | No Backlash | Check Clearance |
| Overheating | Softened Metal | Better Cooling |
6. Does misalignment drive your spur gear failure?

When shafts are not perfectly parallel, the load concentrates on one end of the teeth which often leads to failure. You can detect this issue by looking for a diagonal wear pattern across the tooth face instead of a centered mesh. It gets better. This uneven loading creates stress levels that are much higher than what your gears were designed to handle.
- Use dial indicators for checking shaft parallelism.
- Inspect for corner chipping on the gear teeth.
- Verify the housing is flat and not distorted.
- Record contact patterns during the initial startup.
Key Takeaway
Misalignment concentrates operational loads on small areas of the gear teeth, leading to rapid surface distress and structural failure.
| Alignment Type | Physical Sign | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel | Edge Loading | Re-shim Feet |
| Angular | Diagonal Wear | Adjust Bolts |
| Dynamic | Intermittent Noise | Replace Bearings |
7. Is metal fatigue the root of spur gear failure?

Metal fatigue represents a silent and progressive process that leads to a sudden and often catastrophic spur gear failure. Every time the teeth mesh, they experience a cycle of stress that slowly creates microscopic cracks deep within the steel structure. This is where it gets interesting. Using magnetic particle inspection can reveal these hidden dangers before they reach the surface and cause a failure.
- Inspect fracture surfaces for beach mark patterns.
- Verify the metal has no hidden internal inclusions.
- Check for consistent grain size across the gear teeth.
- Measure the surface hardness with a calibrated tester.
Key Takeaway
Metal fatigue is a progressive failure driven by cyclic stresses that requires advanced non-destructive testing to detect before a structural break occurs.
| Fatigue Feature | Diagnostic Clue | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Smooth Origin | Start of crack | Stress concentration |
| Beach Marks | Slow growth | Normal duty cycles |
| Rough Area | Fast fracture | Ultimate load reached |
8. Why do shock loads cause spur gear failure?
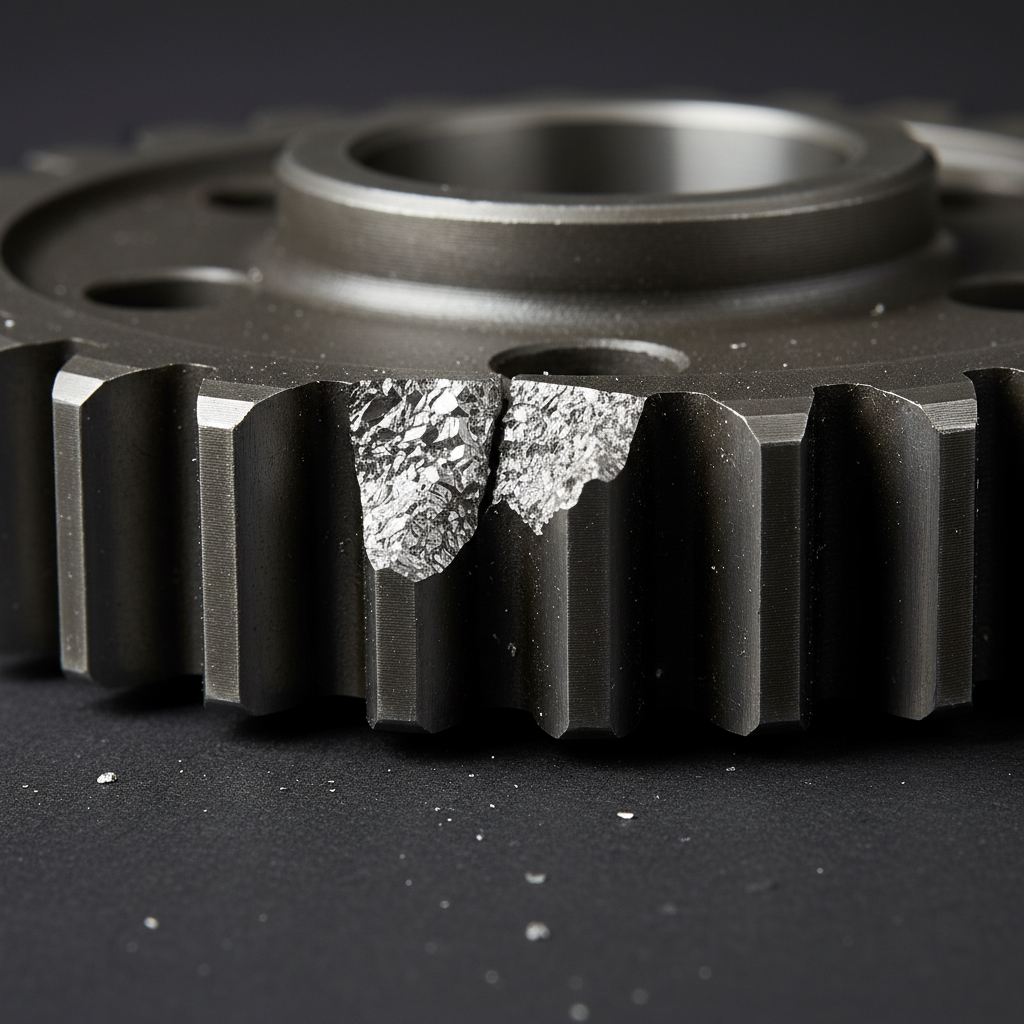

A single massive impact can cause an instant breakdown that shatters teeth and bends shafts within your industrial transmission system. Unlike fatigue, shock failures happen without warning and often leave a rough and crystalline fracture surface across the entire break zone. Ready for the good part? You can install torque limiters to protect your valuable gear sets from these unpredictable events.
- Identify broken teeth with no signs of wear.
- Check for bent shafts or damaged bearing seats.
- Inspect the housing for cracks after a major jam.
- Verify the operation of all mechanical safety devices.
Key Takeaway
Shock loads trigger instant brittle fractures that you can only prevent through robust safety factors and mechanical torque protection devices.
| Failure Mode | Appearance | Primary Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Shear | Clean snap | Massive Overload |
| Shatter | Multiple pieces | Brittle Material |
| Bending | Plastic strain | Ductile Failure |
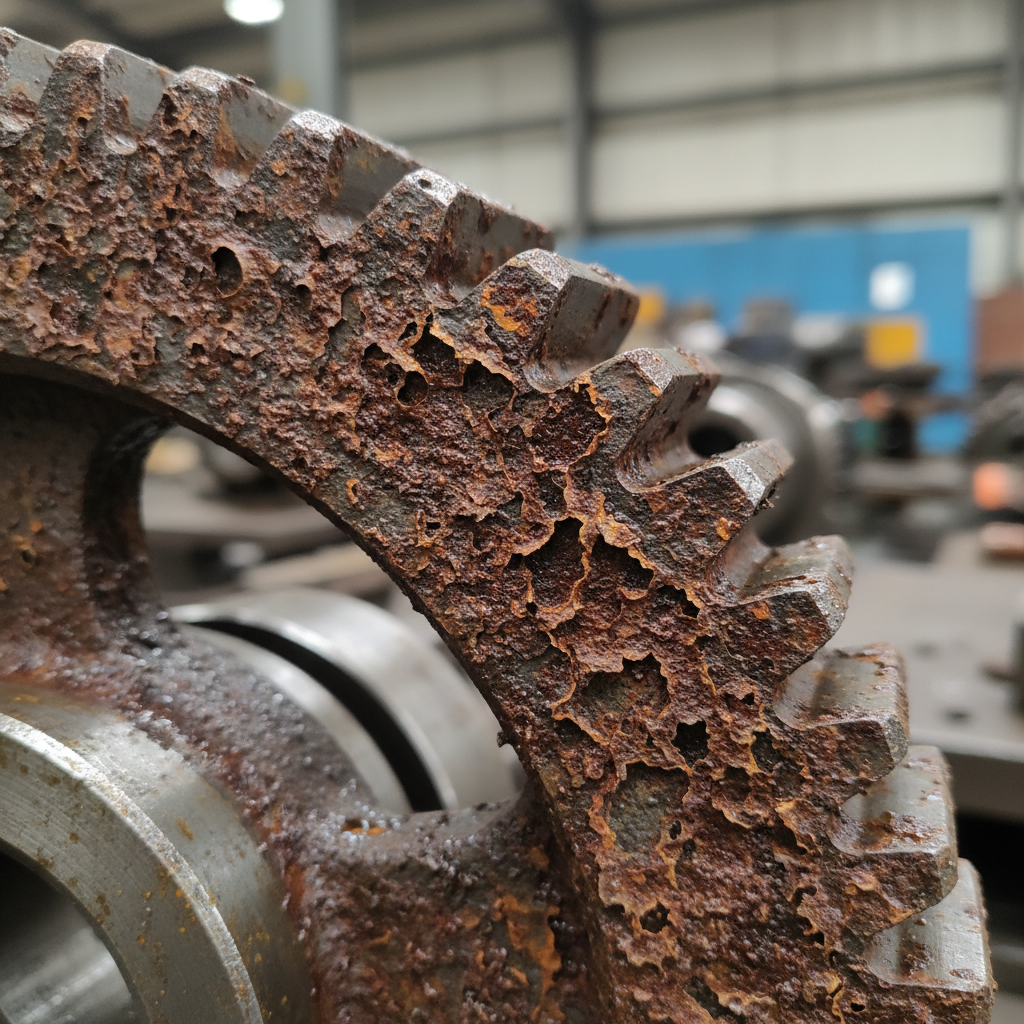

Chemical attack from moisture or acidic oil can trigger a silent and dangerous spur gear failure. Corroded gears create more friction and heat which further degrades your lubricant and accelerates the overall destruction of your drive system. But here is the kicker. Preventing moisture entry is much cheaper than fixing the deep structural damage caused by long-term chemical corrosion.
- Monitor for reddish-brown deposits on gear teeth.
- Check oil for water using the crackle test or lab analysis.
- Inspect for dark stained patches on the tooth flanks.
- Verify the integrity of all gearbox seals and gaskets.
Key Takeaway
Corrosion creates surface pits that serve as stress risers for fatigue cracks, requiring strict moisture control and additive management to prevent failure.
| Corrosion Type | Sign of Damage | Common Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Rusting | Red/Brown spots | Moisture entry |
| Acid Etch | Dark staining | Aged lubricant |
| Chemical Pit | Deep craters | Corrosive fumes |
10. How to document every spur gear failure?
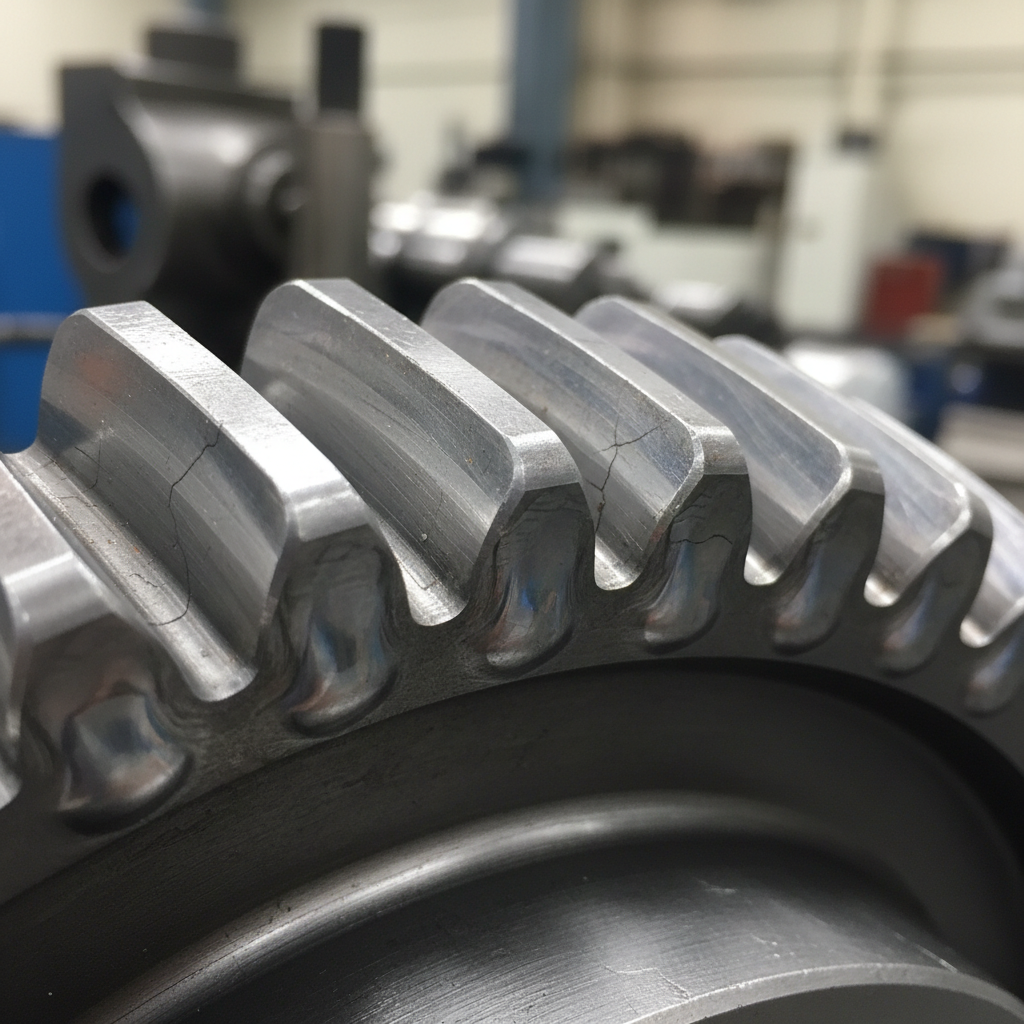

Creating a detailed record of every mechanical breakdown is the only way to prevent a future failure in your facility. You must capture clear photos and collect samples before you clean the parts or take the gearbox apart for a deep repair. Think about it. Once the evidence is gone, it is almost impossible to prove what really caused the failure.
- Take high-resolution photos of all damaged gear teeth.
- Label and save lubricant samples for laboratory analysis.
- Record the operating hours and the load at the time of failure.
- Interview the operators to find out exactly what happened.
Key Takeaway
Thorough documentation preserves critical evidence and provides a systematic roadmap for implementing permanent technical solutions to prevent future gear failures.
| Document Type | Critical Info | Business Value |
|---|---|---|
| Photo Log | Visual Evidence | Faster Diagnosis |
| Lab Report | Material Data | Supplier Accountability |
| Final Summary | Recommended Fix | Permanent Solution |
Conclusion
Mastering the art of gear failure analysis puts you in control of your facility’s reliability and bottom line. You now have the tools to identify whether a problem started with a lubrication error or a simple misalignment during installation. By following a structured approach, you transform from a reactive mechanic into a proactive asset manager who saves time and money. Do not wait for the next loud bang on your factory floor to take action on your mechanical health. Ensure your systems stay operational and efficient by partnering with experts who understand the science of power transmission. For professional support or specialized gear components please contact us today to discuss your specific industrial needs and secure your equipment’s future.
FAQ Section
Q1: Can I prevent spur gear failure entirely?
While you cannot stop all wear, you can significantly extend gear life through proper lubrication, precise alignment, and regular monitoring. Most catastrophic breaks result from neglected maintenance or operating the equipment far beyond its rated capacity in the field.
Q2: What is the best lubricant for gears?
The best lubricant depends on your specific speed, load, and temperature requirements as defined by the equipment manufacturer. Generally, you want a high-quality mineral or synthetic oil with extreme pressure additives that matches the required ISO viscosity grade for your climate.
Q3: How often should I inspect teeth?
You should perform a visual check every few months and a more detailed inspection with oil analysis every six months for critical machinery. High-speed or high-load systems might require monthly vibration monitoring to catch early signs of fatigue.
Q4: Can I use vibration analysis to detect a cracked tooth?
Yes, vibration sensors pick up subtle frequency changes long before your eyes see damage. You will notice increased amplitudes at the gear mesh frequency when teeth become worn or chipped, providing an early warning system for a potential failure.
Q5: What is the best way to stop corrosion in storage?
The best way to prevent corrosion during storage or shipping is to use vapor-phase corrosion inhibitors inside the gearbox housing. Additionally, keeping the unit in a climate-controlled area and ensuring all breathers are sealed will prevent moisture from attacking the metal surfaces.
